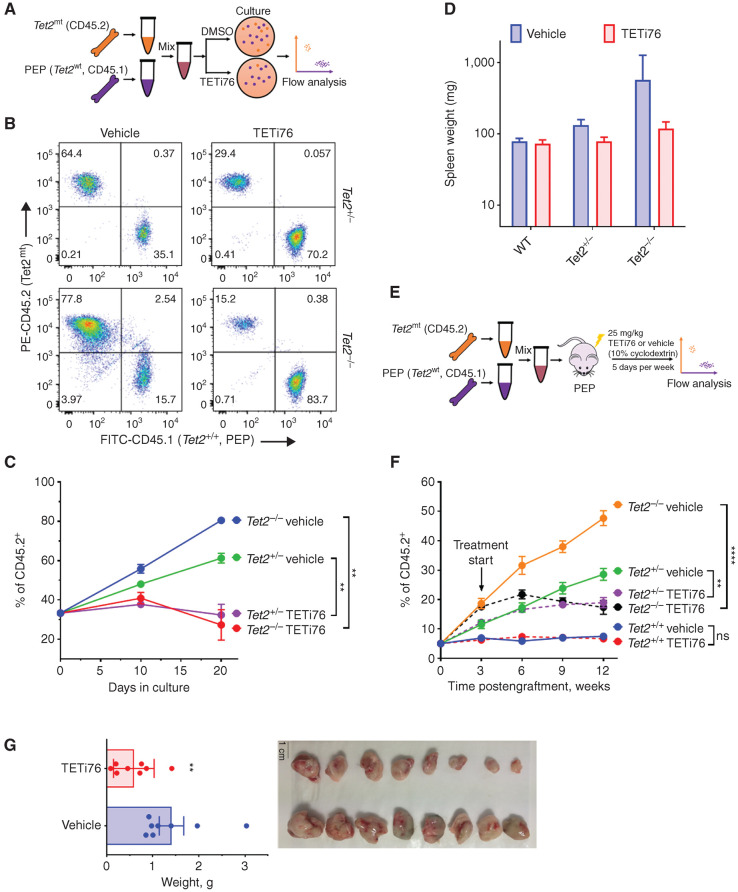
Figure 4.
TETi selectively restricts the growth of TET2-mutant cells. A, Schematic representation of the mixing experiment of Tet2wt and Tet2mt murine bone marrow in a colony-forming assay. B, Tet2mt bone marrow (CD45.2) cells were mixed in a ratio of 1:2 with Tet2+/+ (CD45.1) and grown in MethoCult for colony formation in the presence or absence of TETi76 (20 μmol/L). On day 10, cells were harvested and the ratio of Tet2mt/Tet2+/+ was measured by flow cytometry using isoform-specific antibodies. C, The ratio was plotted for two consecutive platings. D, Tet2mt or TET2wt mice weretreated with TETi (50 mg/kg, p.o., 5 days/week) for 8 weeks. The spleens were harvested, and weights were plotted compared with vehicle control. E, Schematics of experimental design for in vivo transplant experiment. F, C57BL6 Pep Boy mice expressing CD45.1 surface marker on mononuclear hematopoietic cells were lethally irradiated and transplanted with a mixture of donor mouse bone marrows (5% Tet2−/−, CD45.2; and 95% Tet2+/+, CD45.1). Once mice fully recovered after transplant, the engraftment was accessed by isotype-specific antibodies, and TETi treatment (25 mg/kg, s.c.) 5 days a week at 4 weeks was started. The engraftment of Tet2mt cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was monitored and plotted. TETi76 prevented the clonal expansion of Tet2mt cells in vivo. G, Tumor growth of SIG-M5 cells in NSG mice (n = 8/group) was monitored upon TETi76 treatment. Once controlled reached the maximum allowed limit of tumor (<18 mm diameter) burden, tumors were harvested and tumor weight is plotted. TETi76 significantly reduced the tumor size. Data, mean ± SEM; statistical significance (P values) from two-tailed t test is indicated; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.