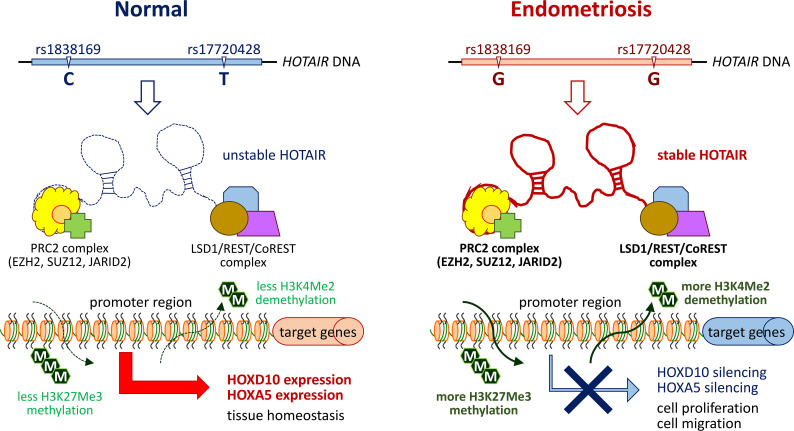
Fig 5. Schematic summary of a proposed model depicting functional impacts of HOTAIR genetic variations on endometriosis development.
Genetic variations at SNP sites, rs1838169 (C to G) and rs17720428 (T to G), in HOTAIR are frequently detected in patients with endometriosis. Such genetic substitutions alter thermo-stability of mature HOTAIR and stabilize its RNA structure. Through epigenetic silencing by H3K27 tri‐methylation or H3K4-demethylation, higher HOTAIR levels in endometriosis patients can down-regulate its down-stream effectors, such as HOXD10 and HOXA5, leading to increased cell proliferation and migration/invasion.