Fig. 8. Lynx1-mediated suppression of nicotinic tone from adolescence in Fmr1 KO mice restores local/long-range input imbalance of ACAVIS neurons and attentional behavior.
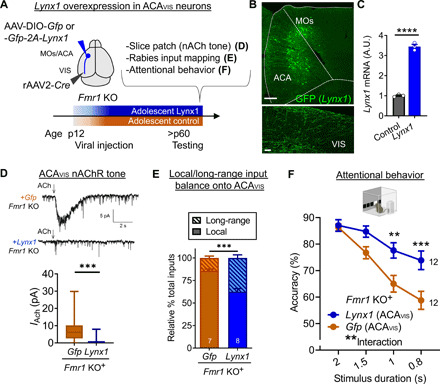
(A) Experimental design: A Cre-dependent Lynx1 overexpression or Gfp control AAV construct was injected in ACA, and retrograde rAAV2-Cre was injected in VIS at p12 in Fmr1 KO mice. (D) nAChR tone, (E) local and long-range input balance, or (F) attentional behavior (5CSRTT) was assessed in adulthood. (B) Representative images showing GFP + ACAVIS neurons in ACA (scale bar, 200 μm) and their terminals in VIS (scale bar, 5 μm). (C) Validation of AAV construct for cre-dependent Lynx1 overexpression. qPCR shows cortical overexpression of Lynx1 mRNA in vivo compared to noninjected native control (t test, t4 = 22.29,****P < 0.0001, three mice each). (D) Top: Representative traces of whole-cell patch recording of ACAVIS neurons overexpressing Lynx1 or a control vector. Bottom: Nicotinic response in adult Fmr1 KO mice [linear mixed model (rank-based), t33 = 4.81,***P < 0.0001; +Gfp: 23 cells per seven mice; +Lynx1: 20 cells per five mice]. (E) Rabies virus–mediated monosynaptic input mapping showed decreased percentage of local connectivity following Lynx1 overexpression from adolescence in adult Fmr1 KO mice (t test, t13 = 5.453,***P = 0.0001; +Gfp: seven mice; +Lynx1: eight mice). (F) Adult Fmr1 KO mice with Lynx1 overexpression in ACAVIS neurons showed an increase in accuracy [two-way repeated measures ANOVA, group × stimulus duration: F3,66 = 5.992, **P = 0.0011; post hoc Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (0.8 s): ***P = 0.0006; 1 s: **P = 0.0055; +Lynx1: 12 mice; +Gfp: 12 mice].
