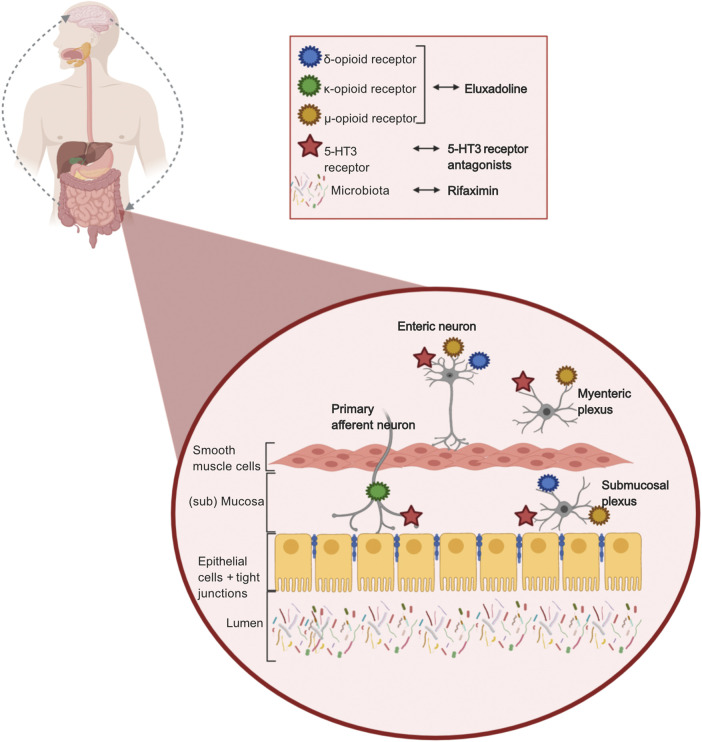
FIGURE 2.
Mechanisms of action of pharmacological treatments in IBS-D. 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, targeting 5-HT3 receptors located on enteric neurons, myenteric plexus, submucosal plexus, and primary afferent neurons, reducing sensory signals, secrotory and motor reflex in the gut. Eluxadoline (opioid receptors agonist), targeting δ-,µ-, and κ-opioid receptors located on enteric neurons, myenteric plexus, submucosal plexus, and primary afferent neurons delaying transit by reducing secretory and sensory signals. Rifaximin, targeting the luminal gut microbiome due to its non-absorbable and non-systemic properties. Created with BioRender.com.