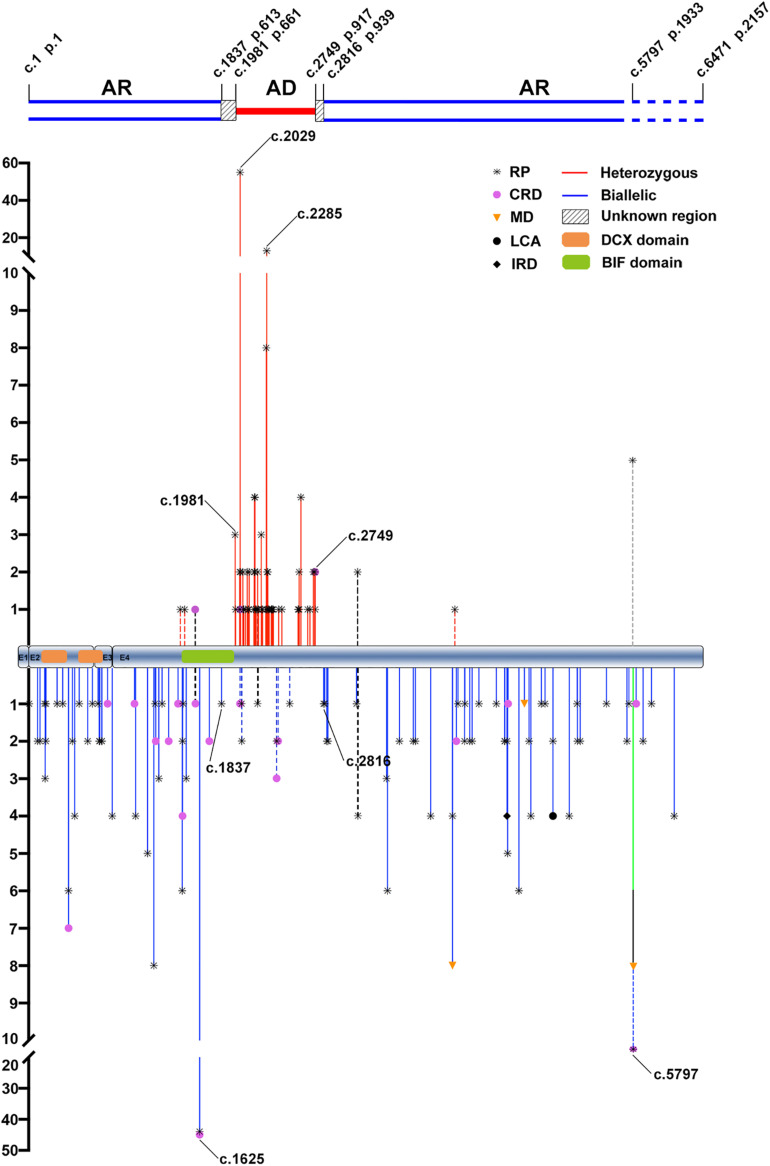
FIGURE 1.
The distribution and frequency of the potential pathogenic truncation variants in RP1 identified in the present and previous studies. AR, autosomal recessive; AD, autosomal dominant; RP, retinitis pigmentosa; CRD, cone-rod dystrophy; MD, macular degeneration; LCA, Leber congenital amaurosis; IRD, inherited retinal disease. The positions and allele counts of the heterozygous RP1 variants are displayed above, while those of the biallelic RP1 variants are displayed below. The two blue lines above represent the autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa (arRP) region, the single red line represents the autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (adRP) region, and the diagonal line between them represents the unknown regions. The two blue dashed lines are used to indicate the pathogenicity of homozygous truncations around the c.5797, and thereafter, need to be further clarified. DCX domain: c.106–354 (p.36–188) and c.460-699 (p.154–233). BIF domain: c.1456–1959 (p.486–653).