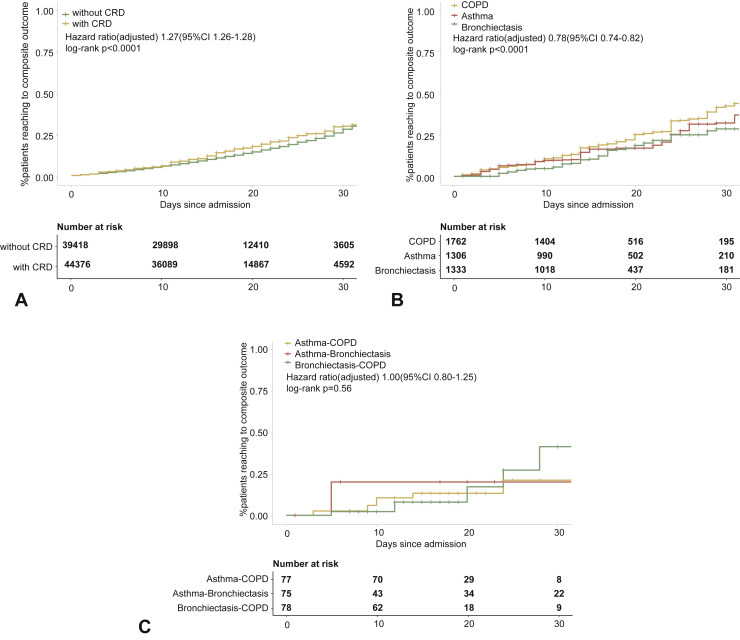
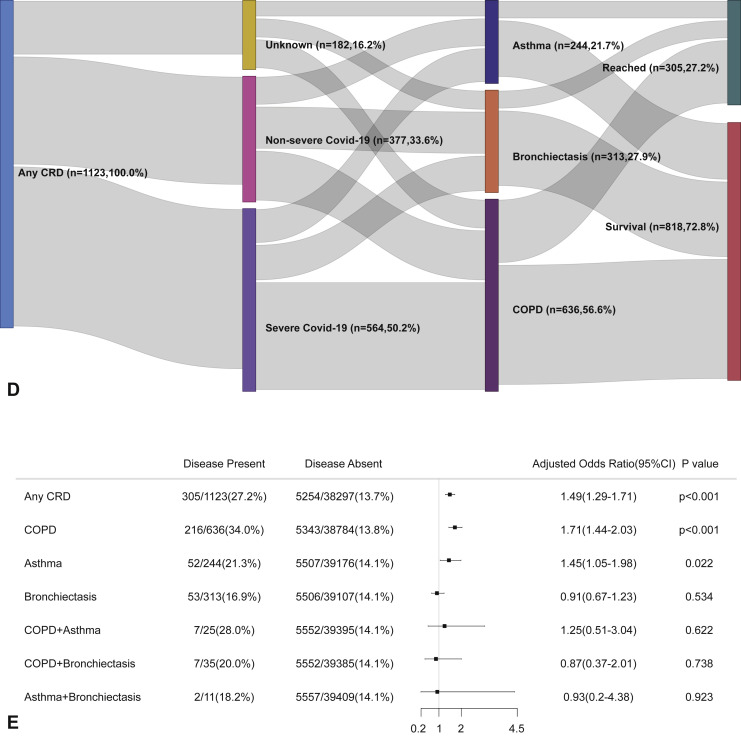
Figure 2.
CRD and the composite outcomes of COVID-19 in the adjusted model. (A) The cumulative rate of reaching to the composite endpoints among patients with or without CRD based on the Cox proportional hazards model. (B) The cumulative rate of reaching to the composite endpoints among patients with or without asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or bronchiectasis based on the Cox proportional hazards model. (C) The cumulative rate of reaching to the composite endpoints among patients with asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-bronchiectasis overlap, and asthma-bronchiectasis overlap based on the Cox proportional hazards model. (D) Association between the severity of COVID-19, CRD, and clinical outcomes. The vertical colored bars represented the patient cohort, which was further categorized into different subgroups. The association between the different subgroups was presented with the gray bars, with greater width representing a greater magnitude of overlap. E, Risk factors predicting the composite endpoints in patients with COVID-19. Shown are the numbers and percentages of patients with each of the category of disease who had reached to the composite endpoint during the study and of patients who had not reached to the composite endpoint. All models have been adjusted with female sex, age, and the presence of any other systemic comorbidities. CI, Confidence interval; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CRD, chronic respiratory disease; OR, odds ratio.