FIGURE 1.
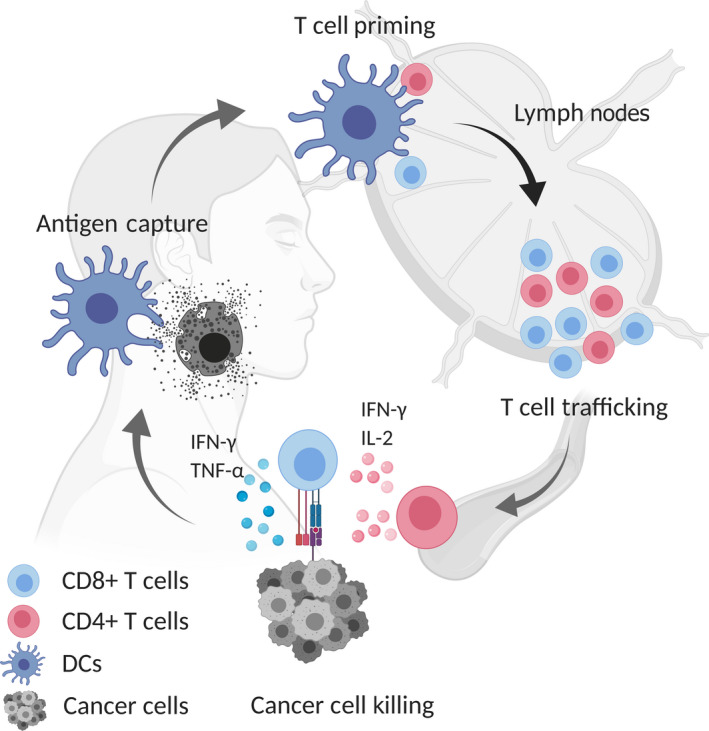
Cancer immunity cycle. The cancer immunity cycle is composed of several phases. Tumor antigens from dying/necrotic tumor cells are captured by tissue migrating antigen‐presenting cells (APCs), in particular dendritic cells (DCs) (conventional type 1 and type 2 DCs) through phagocytosis or endocytosis. Subsequently, APCs traffic into the lymph nodes where antigen‐specific T cells are primed and T cell trafficking to the tumor is induced. Tumor‐specific CD4+/CD8+ T cells cooperatively eradicate cancer cells by recognition of cancer‐specific antigens. IFN‐γ, interferon‐gamma; IL‐2, interleukin‐2; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α
