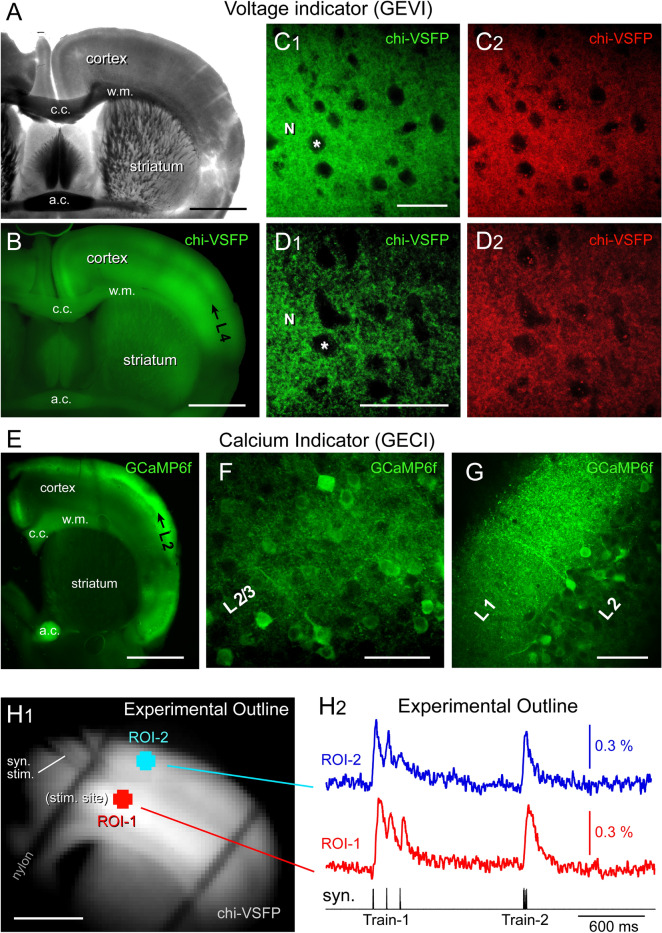
Figure 1.
Transgenic animals. (A) Transgenic animal expressing a GEVI variant called “chi-VSFP”. P151 days, Male. A coronal section captured in transmitted light. Scale, 1 mm. (B) Same brain section as in (A), wide-field fluorescence (GFP filters). Black arrow marks cortical layer 4 (L4). “c.c.”—corpus callosum; “w.m.”—white matter; “a.c.”—anterior commissure. (C1) Confocal image of the somatosensory cortex (layer 2/3) in green channel (excitation 488 nm, emission 510–545 nm). “N”—marks neuropil. “Asterisk”—marks neuronal cell body. Scale, 50 µm. (C2) Same as in (C1) except the emission window is now 578–625 nm. (D1,D2) Same as in (C1,C2) except the location is cortical layer 5. Scale, 50 µm. (E) Transgenic animal expressing a GECI variant called “GCaMP6f”. P254 days, Male. (F) Confocal image of the somatosensory cortex (layer 2/3) in green channel (excitation 488 nm, emission 510–545 nm). Scale, 50 µm. (G) GCaMP-positive neuropil in cortical layer 1. (H1) One video frame obtained with data acquisition camera (80 × 80 pixel) during a voltage imaging trial (cropped). Transgenic animal expressing chi-VSFP, age P210 days, Female. Scale, 1 mm. Syn. Stim—marks a glass stimulation electrode entering the brain slice. (H2) Synaptically-evoked optical signals from two regions of interest (ROIs). ROI-1 is at the stimulation site, in cortical layer 5. ROI-2 is selected form L2/3. Each trace is product of temporal averaging (4 sweeps), low-pass filtering (40 Hz cutoff, Gaussian), bleach subtraction (exponential fit) and high-pass filtering (Tau Filter = 10). Synaptic stimulation Train-1 consists of three electrical pulses at 120 ms ISI, while Train-2 employs a 12 ms ISI.