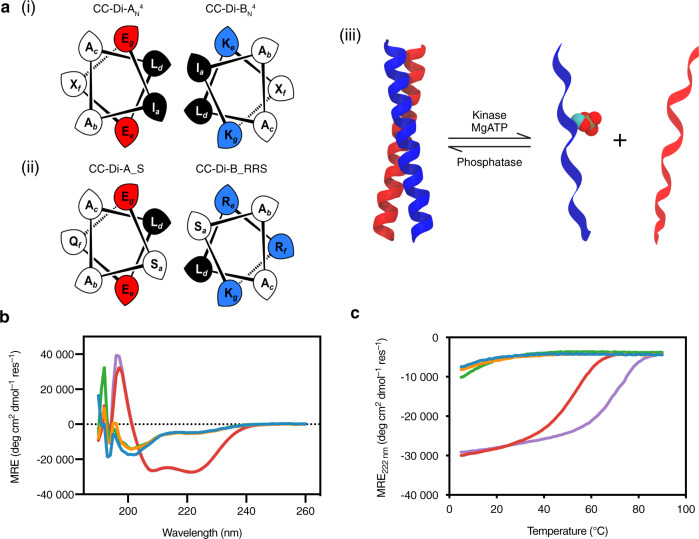
Fig. 1. Design and solution-phase characterization of phosphorylation-switchable coiled-coil heterodimers.
a Helical wheels for the (i) parent and (ii) CC-Di-A_S:CC-Di-B_RRS coiled-coil (CC) designs, and (iii) illustration of the switching concept. In its unphosphorylated state, CC-Di-B_RRS (blue) forms a heterodimeric CC with CC-Di-A_S or CC-Di-AN4 (red). Phosphorylation of CC-Di-B_RRS by a protein kinase (e.g. PKA) prevents this dimerization due to the bulk and charge of the phosphoryl moiety. Dephosphorylation by a protein phosphatase (e.g. lambda protein phosphatase) re-enables dimerization. b CD spectra of individual peptides and their combinations acquired at 25 °C in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at pH 7.4: blue, CC-Di-A_S; orange, CC-Di-AN4; green, CC-Di-B_RRS; red, CC-Di-A_S:CC-Di-B_RRS; and purple, CC-Di-AN4:CC-Di-B_RRS. c Thermal unfolding curves of individual peptides and their combinations in PBS at pH 7.4. The concentration of each peptide was 50 μM in all CD experiments.