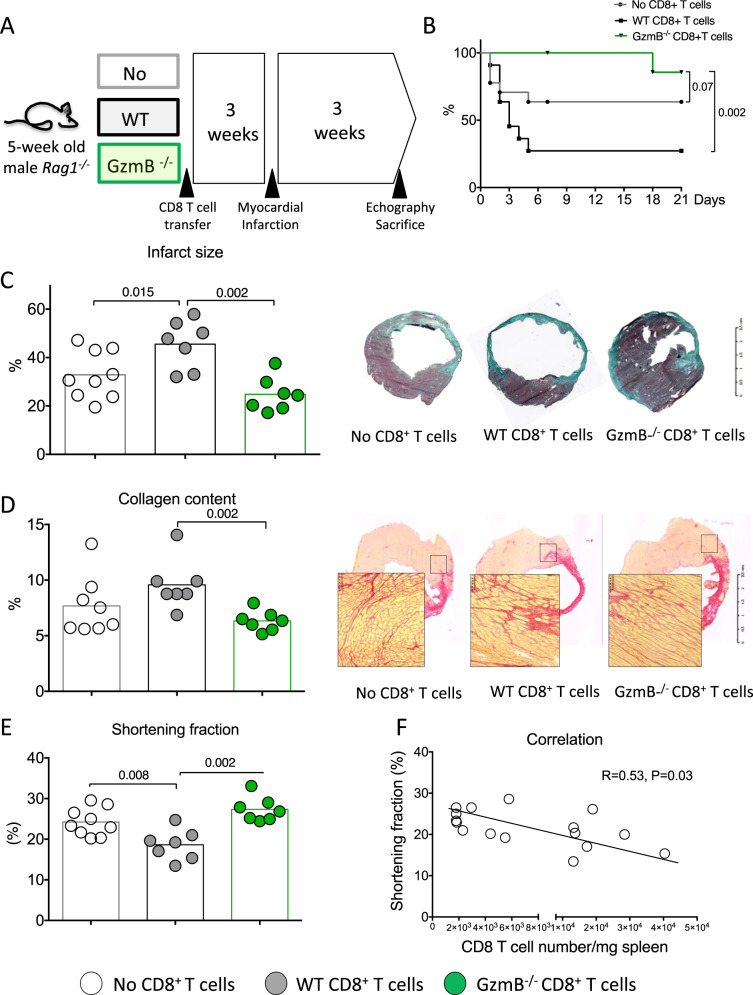
Fig. 5. CD8+ T lymphocytes trigger adverse ventricular remodeling and alter heart function through the production of Granzyme B.
A Rag1−/− mice injected with either CD8-depleted splenocytes (White) or CD8 cell-depleted splenocytes re-supplemented with WT (gray) or GzmB−/− CD8+ T cells (green), 3 weeks before MI. B Survival curves following MI (from 3 experiments, No CD8 n = 15, WT CD8 n = 18, and GzmB−/− CD8 n = 8). C Representative photomicrographs and quantitative analysis of infarct size. D Collagen content in the peri-infarct area in the 3 groups of mice, scale bar 100 μm. Results are pooled from three independent experiments including surviving mice (no CD8 n = 9, WT CD8 n = 7, and GzmB−/− CD8 n = 7). E Echocardiography analysis after 21 days of MI and assessment of LV shortening fraction (SF) in the 3 groups of mice (no CD8 n = 9, WT CD8 n = 7, and GzmB−/− CD8 n = 7). F Correlation between CD8+ T cell number in the spleen at day 21 and LV shortening fraction. Data from CD8-depleted splenocytes or CD8 cell-depleted splenocytes re-supplemented with WT CD8+ T cells have been included (n = 16). P values were calculated using two-tailed Kruskal-Wallis test (C, D, E). Difference in survival was evaluated using log-rank test (B) and correlation was studied using Spearman’s test (F).