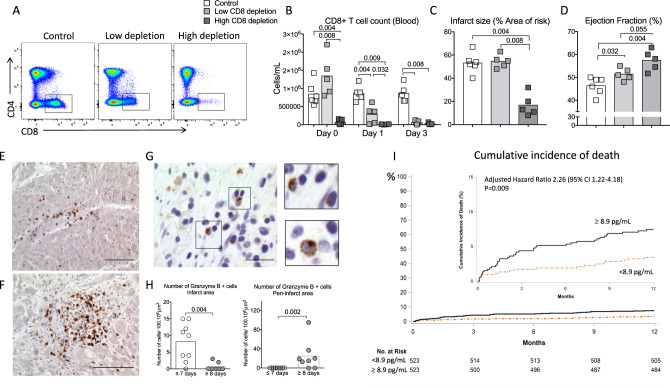
Fig. 6. Pathogenic role of CD8+ T cells in a model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in pig and relevance to the human disease.
A Flow cytometry analysis of blood CD4+ T and CD8+ T subsets at day 1 after MI in control (PBS, CTR, n = 6), low (light gray, n = 5), and high (dark gray, n = 5) CD8-depleted groups. B Quantification of CD8+ T cell count in the blood at baseline, day 0, day 1, and day 3 after MI. C Representative picture and quantification of infarct size at day 14 in control, low, and high CD8-depleted groups. D Quantitative evaluation of left ventricle ejection fraction (Simpson) of CTR or CD8-depleted pigs. E, F Detection of CD8+ T cells (brown) in human heart biopsy of MI patients, using immunohistochemistry at day 3 (E, upper) and day 8 (F, lower) after MI, scale bar 50 μm. G Detection of GRANZYME B+ cells (brown) in human heart biopsy of MI patients, using immunohistochemistry, scale bar 20 μm. H Quantification of GRANZYME B+ cells (brown) in human heart biopsy of MI patients, using immunohistochemistry at different time points (n = 9 day ≤ 7, n = 8 day ≥ 8). I Survival according to baseline circulating GRANZYME B level (< or > median value) in patients with acute MI (n = 1046). High level of GRANZYME B at the admission for acute MI were independently predictive of death after 1 year of follow-up after multiple adjustments (see Methods and Supplementary Table 3). HR = hazard ratio. P values were calculated using two-tailed Mann-Whitney test (H) or Kruskal-Wallis test (B–D).