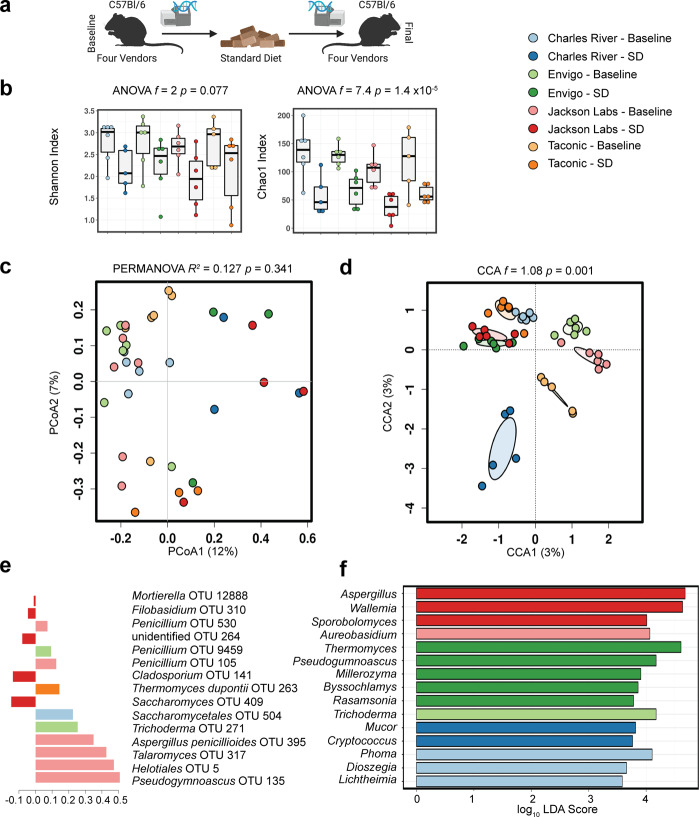
Fig. 1. Gut fungal communities cluster by vendor, age, and dietary exposure.
a Experimental schematic. b Compared to healthy mice exposed to a standardized chow diet for 8 weeks, baseline community diversity is higher in mice upon delivery from vendors. While gut fungal communities remained distinctly clustered by vendor, exposure to a standardized chow diet for 8 weeks exerted a convergent effect on community composition (c, d Bray–Curtis dissimilarity distance). Supervised partial least squares discriminant analysis (e) and linear discriminant analysis of effect size (f) confirm key operational taxonomic units and genera driving differences in community composition. Hypothesis testing was performed using ANOVA (b), PERMANOVA (c), and CCA (d). CCA canonical correspondence analysis, OTUs operational taxonomic units, SD standard diet, PERMANOVA permutational multivariate ANOVA, PCoA principal coordinates analysis. Schematic created using BioRender.com.