Table 2.
Analyses of Associations of Body Mass Index With Beta-Diversity at Taxonomic Level 6 (Genus)a
| Dissimilarity | Standard Reference Method | MiRKAT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
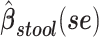
|
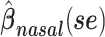
|
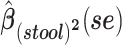
|
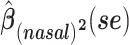
|
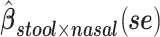
|
2-df P Value |
5-df P Value |
P Value | |
| Bray-Curtis | ||||||||
| Mainb | 2.27(0.98)c | 7.96(5.12) | 0.0406c | |||||
| Quadraticd | 1.62(1.14) | 4.15(10.67) | 6.84(5.89) | −38.98(73.08) | −16.06(47.87) | 0.0012c | 0.0102c | |
| Unweighted UniFrac | ||||||||
| Mainb | 2.67(3.37) | −1.43(3.88) | 0.6696 | |||||
| Quadraticd | −1.41(3.90) | 0.83(4.12) | 62.72(41.06) | 132.7(85.71) | −41.99(94.86) | 0.0116c | 0.0020c | |
| Weighted UniFrac | ||||||||
| Mainb | 2.89(2.25) | 1.90(6.49) | 0.1924 | |||||
| Quadraticd | −3.19(3.34) | −13.41(9.53) | 12.55(20.93) | −223.3(113.60)c | −131.6(102.90) | 2.03 ×10–5c | 0.0347c | |
Abbreviations: df, degrees of freedom; MiRKAT, microbiome regression-based kernel association test; se, standard error; UniFrac, unique fraction.
a Analysis of data from the American Gut Project (12). Regression coefficient estimates and their standard errors (se) are denoted, for example, by 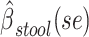 . All analyses include age and sex in the models to adjust for potential confounding by these factors.
. All analyses include age and sex in the models to adjust for potential confounding by these factors.
b Main effects for distance to stool and distance to nasal samples (Xstool and Xnasal; see Methods).
c Statistically significant association at 0.05 level.
d Model also includes (Xstool)2, (Xnasal)2 , and (Xstool) (Xnasal).
