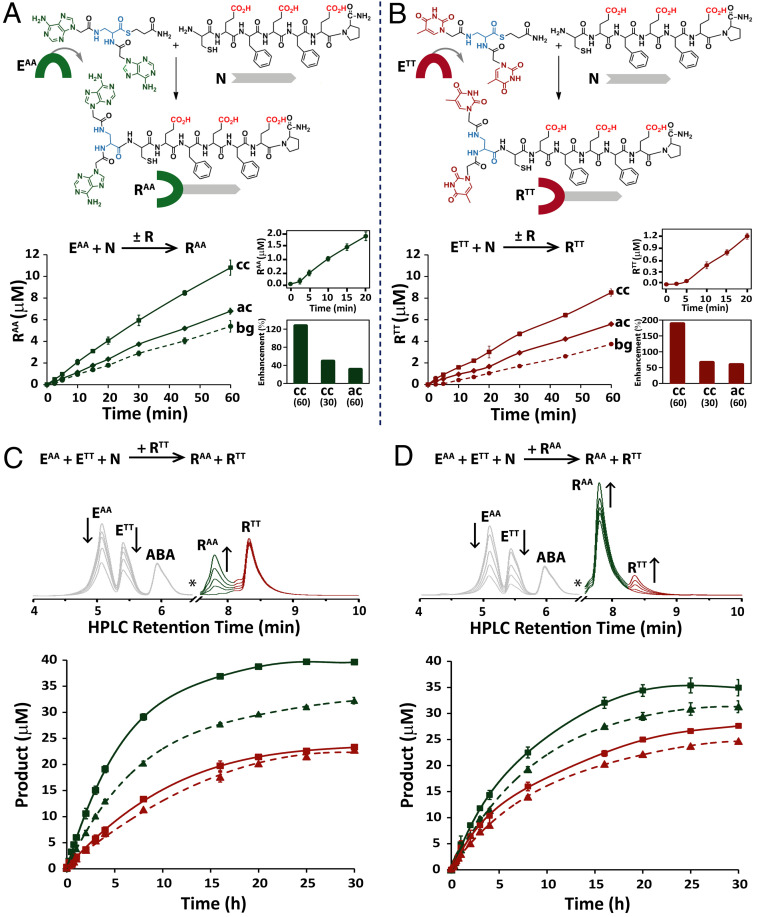
Fig. 1.
Nucleopeptide replication networks. (A and B) NCL reactions forming the RAA and RTT conjugates from their respective electrophile and nucleophile precursors and time-dependent formation of these conjugates in template-free (bg), autocatalytic (ac), and cross-catalytic (cc) reactions. Note that at pH 7.4, the Glu side chain carboxylic acids would be in their deprotonated anionic form. Reactions were carried out with 100 µM EAA or ETT and 100 µM N, either in the absence of a template (bg) or when seeded with the designated amount of template at initiation (ac/cc). Insets show the early stages of the background reactions, highlighting the lag phase typical of product formation through autocatalysis (Top insets) and the rate enhancement (percent) in cross-catalytic reactions seeded with 60 or 30 µM template or in autocatalytic reactions seeded with 60 µM template (Bottom insets). (C and D) A time-dependent analysis of the replicator-assisted product formation of the conjugates RAA (green) and RTT (red) in network reactions initiated with EAA (50 µM), ETT (50 µM), and N (100 µM) and seeded with 20 (dashed lines) or 60 μM (solid lines) RTT (C) or RAA (D). HPLC chromatograms (Top) indicate the increase in RAA and RTT product over time in representative reactions seeded with 60 μM RTT (C) or 60 μM RAA (D); note that RTT and RAA peaks have initial intensity due to seeding (in C and D, respectively), and the * symbols denote minor (≥15%) branched product peaks, removed for clarity (see also SI Appendix, Fig. S20). All reactions were carried out in duplicate, in Hepes buffer (pH 7.4), in the presence of TCEP as a reducing agent (5 mM) and with ABA (30 μM) as the internal standard. Data were acquired by HPLC analysis of aliquots collected at the designated times (SI Appendix, Figs. S17–S20).