Fig. 5. Wnt–β-catenin signaling is activated by mTORC1 signaling and responsible for committing CNCCs into an aberrant chondrogenic lineage.
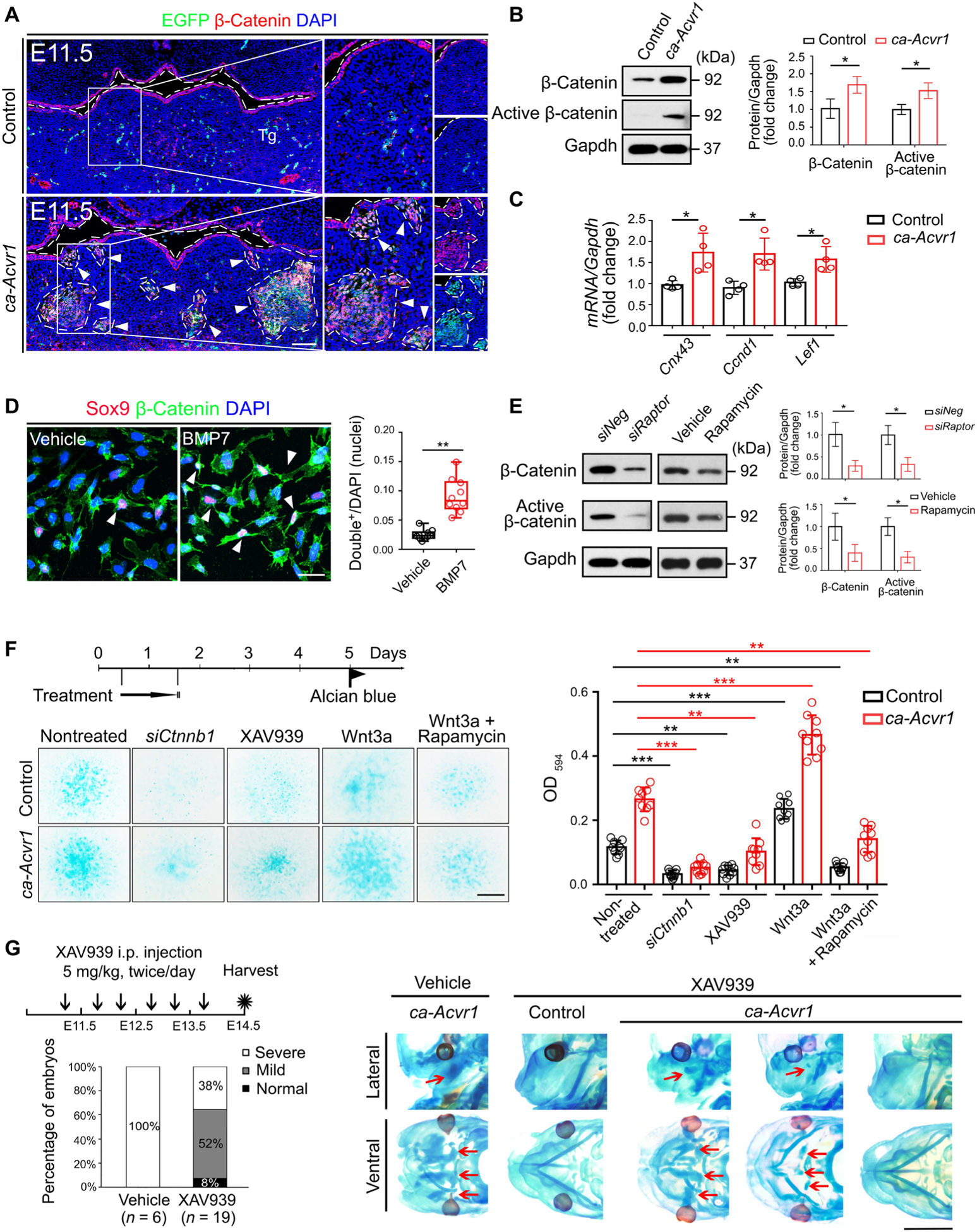
(A) Double immunofluorescence of β-catenin (red) and the ca-Acvr1 transgene marker EGFP (green) in coronal head sections from control and ca-Acvr1 mutant embryos at E11.5. Green signals in control are autofluorescent blood cells. White arrowheads indicate ectopic cartilages. Scale bar, 100 μm. n = 4 mice per group. (B) Western blot analysis and quantification of β-catenin and active β-catenin in control and mutant BA1 tissues. Gapdh is a loading control. n = 4 independent experiments. (C) Relative expression of Cnx43, Ccnd1, and Lef1 in BA1 tissues at E11.5. n = 4 independent experiments. (D) Immunostaining and quantification of Sox9 (red) and β-catenin (green) in the nuclei of BA1 cells from control embryos treated with vehicle or BMP7. White arrowheads indicate Sox9 and β-catenin double-positive nuclei. Scale bar, 20 μm. n = 5 independent experiments. (E) Western blot analysis and quantification of β-catenin and active β-catenin in control or mutant BA1 cells treated with siRaptor or rapamycin for 24 hours. Uncropped Western blot images are shown in fig. S10. n = 3 independent experiments. (F) Experimental scheme for treating control and mutant BA1 cells with siRNA targeting β-catenin (siCtnnb1), the tankyrase inhibitor XAV939, Wnt3a alone, or Wnt3a plus rapamycin for 24 hours; representative images of Alcian blue staining of treated cells; and optical density quantification to assess chondrogenesis. Scale bar, 1 mm. n = 10 independent experiments. (G) Schematic representation, the ratios of each cartilage phenotype (severe, mild, and normal), and representative images of Alcian blue staining of mutant embryos treated in utero with rapamycin from E11.25 to E13.5. The numbers of mutant mice examined are shown in parentheses. Red arrows indicate ectopic cartilages. Scale bar, 2 mm. Error bars are means ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; t test [(B) to (E)]; ANOVA (F).
