Figure 3.
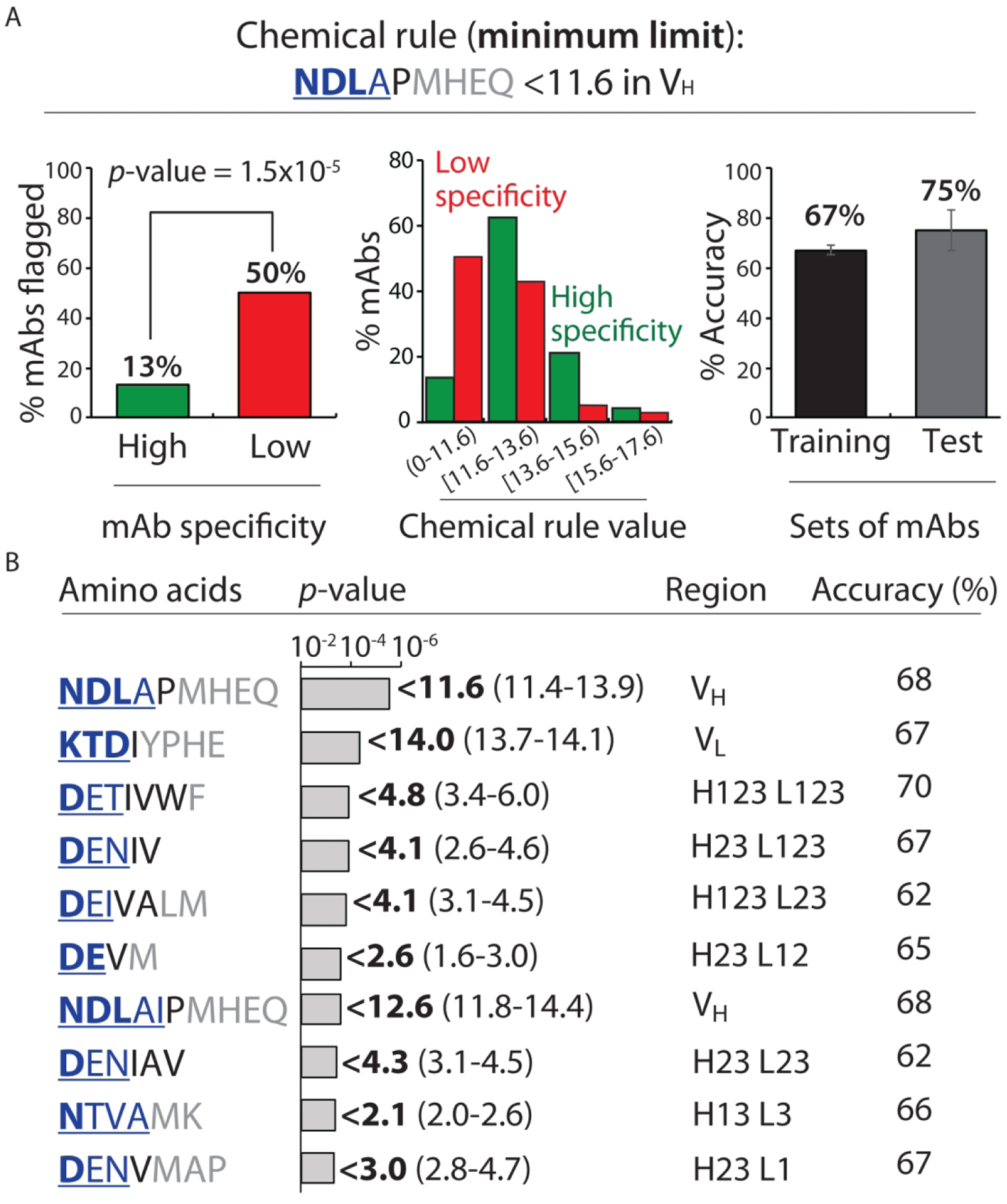
Chemical rules for selectively flagging mAbs with low specificity that limit the minimum allowable number of solvent accessible residues in antibody variable regions. Each chemical rule is a minimum limit on the summed counts of different types of amino acids in the CDRs weighted by their relative solvent accessibilities. (A) Most selective minimum chemical rule for identifying mAbs with low specificity. mAbs with <11.6 Asn, Asp, Leu, Ala, Pro, Met, His, Glu and Gln residues – weighted by their solvent exposures – in VH are flagged. The graphs are presented as described in Fig. 2. (B) Summary of the ten most selective chemical rules that limit the minimum sum of particular types of residues. In (A) and (B), the contributions of the residues to each rule are reported are described in Fig. 2 except that the differences in the observed rule values are calculated for high specific mAbs relative to low specific mAbs. mAbs with low and high specificity are defined as described in Fig. 1. The p-values and accuracies were calculated as described in Fig. 2.
