Figure 4. Antibodies induced through intestinal Candida colonization confer protection against gut-derived and blood-borne systemic candidiasis caused by C. albicans or C. auris.
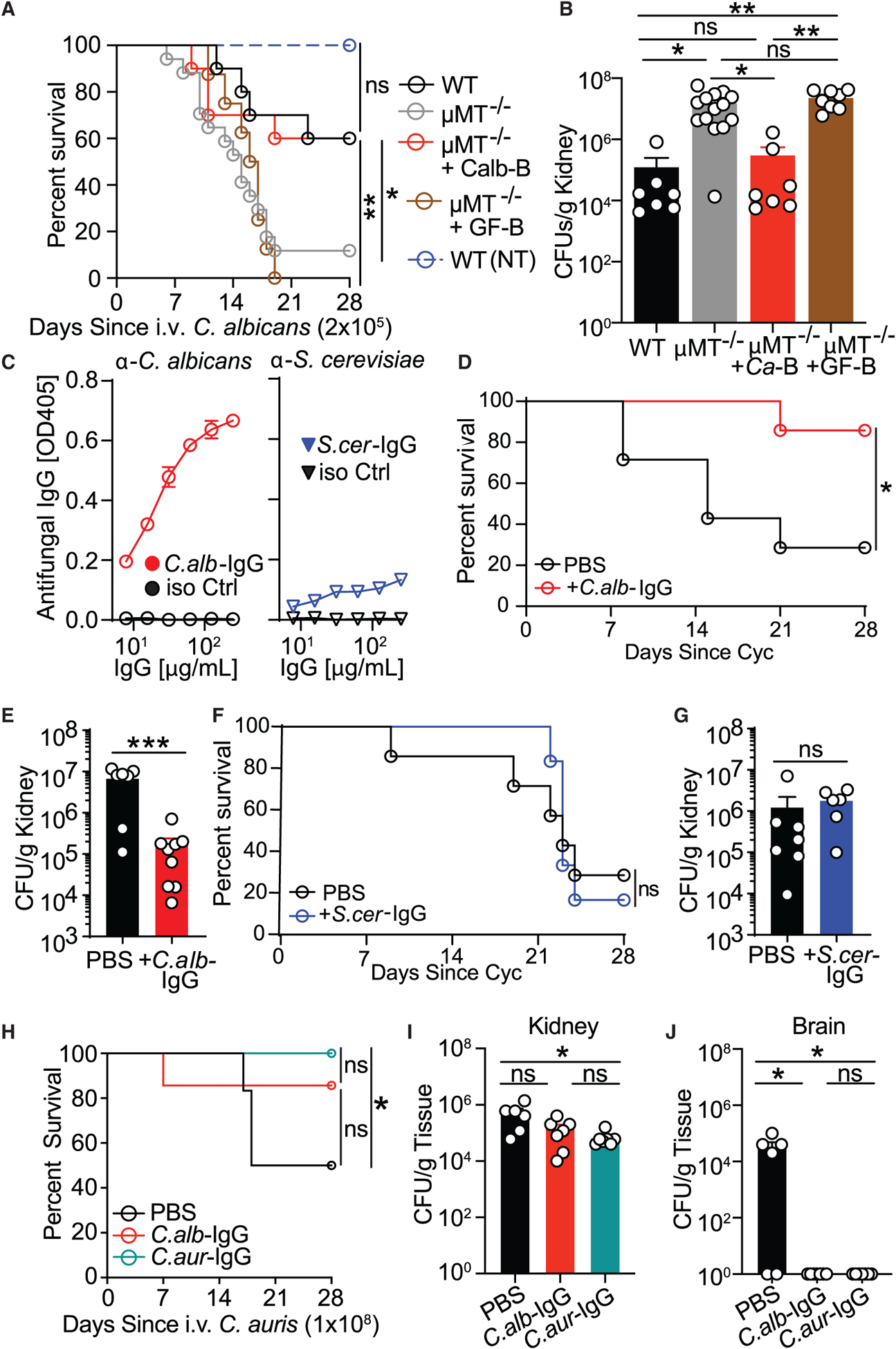
(A and B) WT mice (WT), μMT−/− mice (μMT−/−), and μMT−/− mice adoptively transferred splenic B cells from C. albicans-monocolonized GF mice (mMT−/− +Ca-B) or untreated GF mice (μMT−/− +GF-B) were infected intravenously (i.v.) with C. albicans. A control group of WT mice was left uninfected (WT, NI). Disease morbidity (A) and C. albicans systemic spread to kidney tissue (B) were assessed; log rank Mantel-Cox test (A) and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (B). WT, n = 7; μMT−/−, n = 14; μMT−/− +Ca-B, n = 7; μMT−/− +GF-B, n = 8; WT (NI), n = 5. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
(C) Antibody reactivity assessment against C. albicans and S. cerevisiae lysates of purified serum IgG antibodies from C. albicans- (C.alb-IgG, left panel) and S. cerevisiae- (S.cer-IgG, right panel) monocolonized GF mice, respectively measured by ELISA.
(D and E) C.alb-IgG protection against cyclophosphamide (Cyc)-induced systemic fungal dissemination in SPF mice intestinally colonized with C. albicans (treatment scheme depicted in Figure S4B). Shown are disease morbidity (D) and systemic C. albicans spread into kidney tissue (H). Statistical analysis was performed using log rank Mantel-Cox test (D) or Mann-Whitney test (E). PBS, n = 7; +C.alb-IgG, n = 9.
(F and G) Lack of protection by S.cer-IgG against Cyc-induced systemic fungal dissemination in SPF mice intestinally colonized with C. albicans (treatment scheme depicted in Figure S4B). Shown are survival (F) and systemic C. albicans spread into kidney tissue (G). ns, p > 0.05; log rank Mantel-Cox test (F) and Mann-Whitney test (G). PBS, n = 7; +C.alb-IgG, n = 6.
(H–J) Intestinal GF colonization-induced C.aur-IgG protects mice against systemic infection with C. auris. The effect of C.alb-IgG and C.aur-IgG was assessed after i.v. infection with C. auris. Shown are disease morbidity (H) and systemic C. auris spread into kidney (I) and brain tissue (J). Statistical analysis was performed using log rank Mantel-Cox test (H) or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (I and J). PBS, n = 6; +C.alb-IgG, n = 7; +C.aur-IgG, n = 7. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
Each dot represents an individual mouse. Error bars indicate SEM. ns, p ≥ 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. See also Figure S4.
