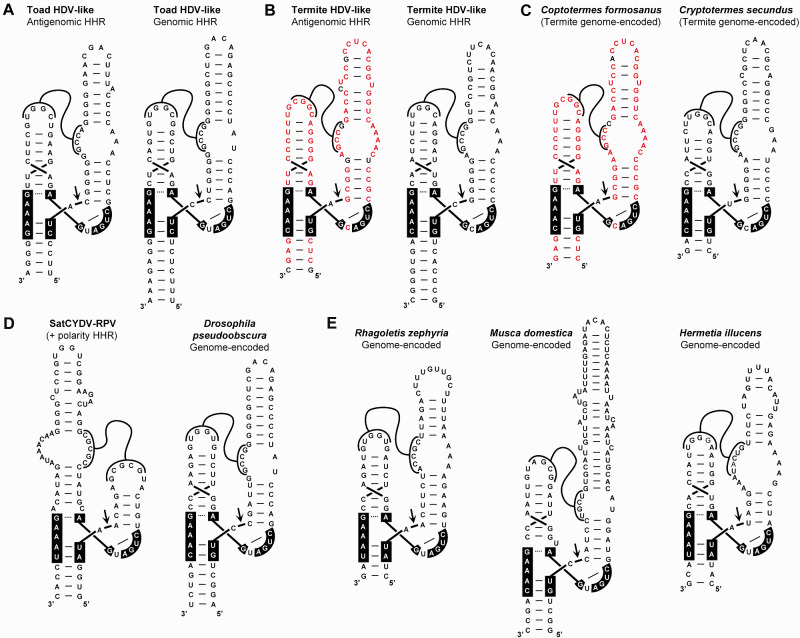
Figure 4.
Secondary structure of the antigenomic and genomic hammerhead ribozymes (HHRs) present in the HDV-like genomes of (A) a toad and (B) a termite. (C) Examples of similar HHRs encoded in the DNA genomes of the termite Coptotermes formosanus (BLKM01010448.1) and Cryptotermes secundus (NEVH01024570.1) species. Sequence identity between the antigenomic HHR from the termite HDV-like RNA and a DNA genome-encoded HHR motif in C. formosanus termite are highlighted in red. (D) Secondary structure of the HHR motifs present in the circRNA Satellite (+ polarity) of the Cereal Yellow Dwarf Virus serotype RPV (SatCYDV-RPV, GenBank: M63666.1) and in the D. pseudoobscura genome (Perreault et al. 2011). (E) Examples of HHRs motifs detected in the genomes of the fruit fly Rhagoletis zephyria, the housefly Musca domestica and the soldier fly Hermetia illucens (de la Peña et al., in preparation).