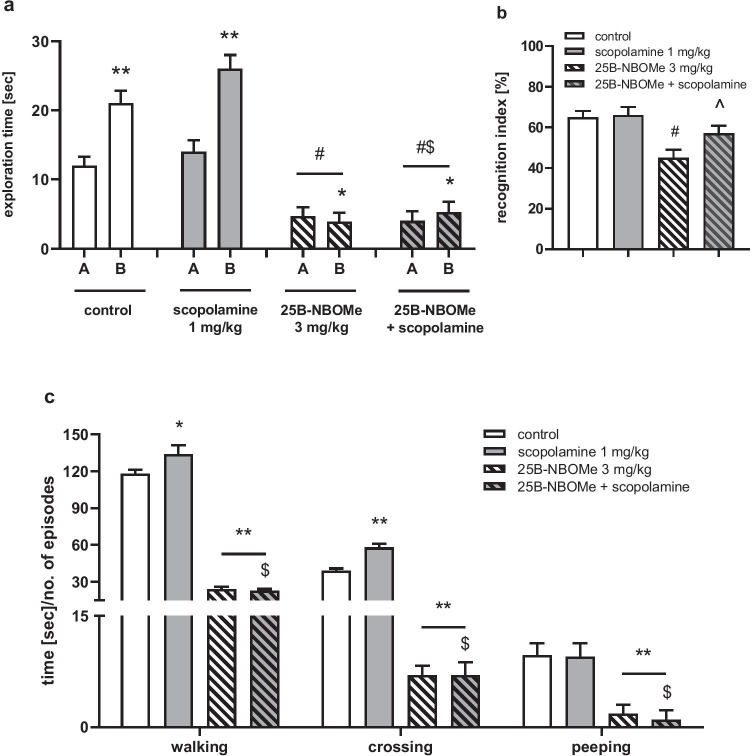
Fig. 7.
The effect of scopolamine (1 mg/kg) on 25B-NBOMe (3 mg/kg)-induced changes in rats’ performance in the novel object recognition (a, b) test and locomotor activity in the open field (c) test. a Exploration time in the recognition session for the familiar (A) and novel object (B). b Ri expressed as the time spent on novel object exploration in relation to the total exploration time of both the novel and familiar objects. c The time spent on walking, the number of episodes of crossing, and the number of episodes of peeping. Values are the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), n = 6–12 per experimental group. a *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 novel vs. familiar object (t test); #p < 0.01 vs. control; $p < 0.01 vs. scopolamine (one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test); b #p < 0.01 vs. control; ^p < 0.01 vs. 25B-NBOMe 0.3 mg/kg (one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test); c *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. control; $p < 0.01 vs. scopolamine (one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test)