Figure 3.
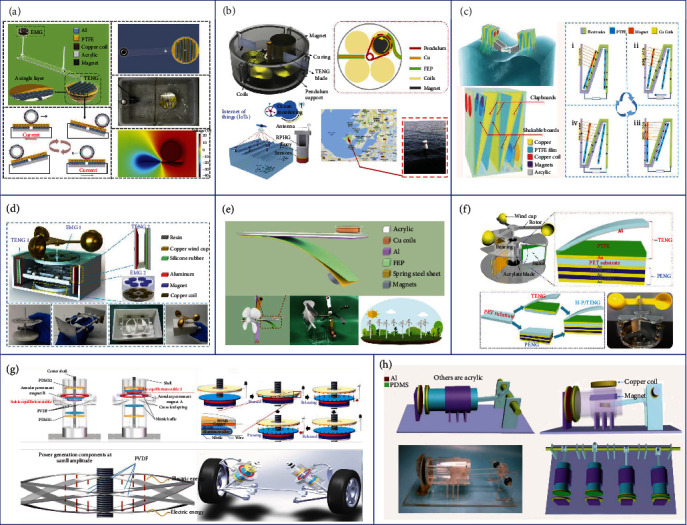
TENG-based hybrid generators for outdoor mechanical energy harvesting. (a) A teeterboard-like TENG-EMG hybrid generator for harvesting low-frequency ocean wave energy. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [95], copyright 2019 Elsevier B.V. (b) A rotational pendulum-based TENG-EMG hybrid generator designed for ultralow-frequency blue energy harvesting. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [96], copyright 2019 Elsevier B.V. (c) A double-swing TENG-EMG hybrid generator for highly efficient wave energy harvesting. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [73], copyright 2019 Wiley-VCH. (d) A TENG-EMG hybrid generator with contact-separation mode TENG for low-frequency wind energy harvesting. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [103], copyright 2019 Elsevier B.V. (e) A windmill-like TENG-EMG hybrid generator for steady and efficient energy harvesting of low-speed wind. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [104], copyright 2020 Springer Nature. (f) A rotational TENG-PENG hybrid generator for highly efficient and stable wind energy harvesting. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [107], copyright 2018 Elsevier B.V. (g) A bistable broadband TENG-PENG hybrid generator for energy harvesting of ambient low-frequency rectilinear motions. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [114], copyright 2019 Elsevier B.V. (h) A crankshaft piston-based TENG-EMG hybrid generator for rotational mechanical energy harvesting. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [115], copyright 2018 Wiley-VCH.
