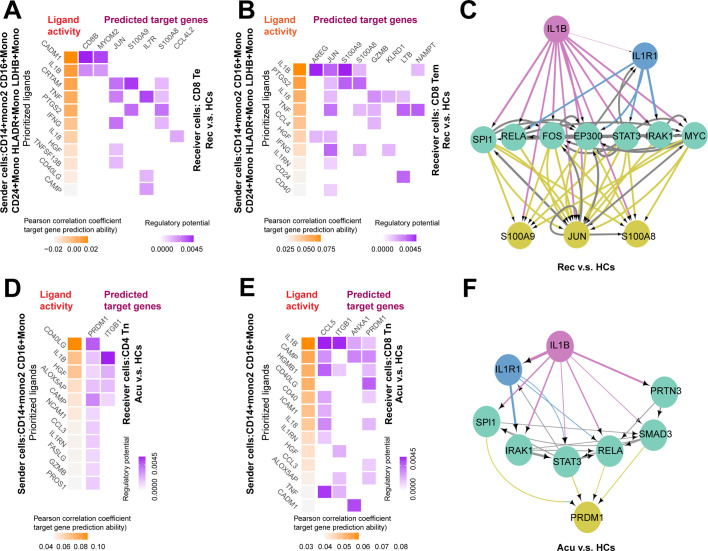
Fig. 6.
Monocytes might facilitate the proliferation and exhaustion of T cells through IL1B signaling pathways.
Heatmap showed the predicted ligand activity and the regulatory potential of the ligand and their target genes. Ligands of CD14+ Mono2, CD16+ Mono, CD24+ Mono, HLA-DR+ Mono and LDHB+ Mono and their target genes in A. CD8+ Te cells, B. CD8+ Tem cells in the recovery stage compared with healthy controls (HCs) (orange: ligand; purple: target genes). C. Network of the potential signaling pathways between the ligand IL1B and it predicted target genes, and the signaling/transcriptional regulators in these paths were visualized in recovery stage. (red: ligand; yellow: target genes; green: signaling/transcriptional regulators; blue: receptor). The thickness of edge line represented the weight of the interactions in the weighted integrated networks. Ligands of CD14+ Mono2, CD16+ Mono and their target genes in D. CD4+ Tn cells, E. CD8+ Tn cells in the acute stage compared with HCs (orange: ligand; purple: target genes). F. Network of the potential signaling pathways between the ligand IL1B and it predicted target genes, and the signaling/transcriptional regulators in these paths were visualized in acute stage. (red: ligand; yellow: target genes; green: signaling/transcriptional regulators; blue: receptor). The thickness of edge line represented the weight of the interactions in the weighted integrated networks. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)