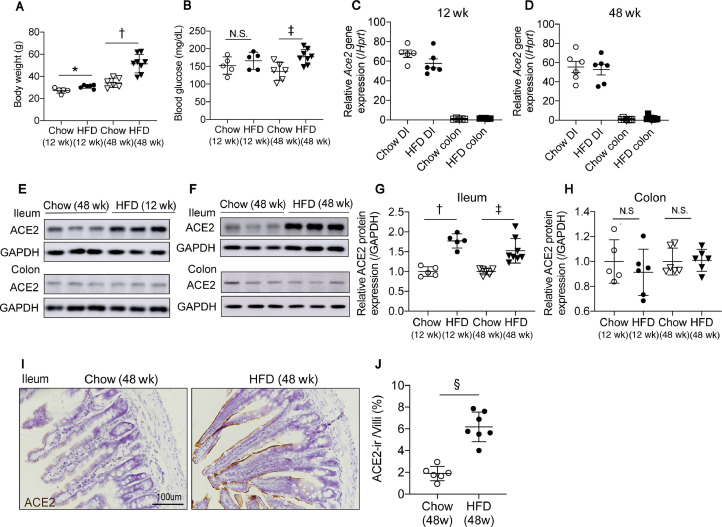
Fig. 1.
ACE2 expression is increased in the ileum of mice fed on HFD. (A) Body weight of mice fed an HFD for 12- and 48-wk. (B) Basal blood glucose level is elevated in mice fed an HFD for 48-wk. (C,D) qPCR shows relative Ace2 mRNA levels are much higher in the ileum than the colon but do not differ between chow- or HFD-fed animals at both time points. (E,F) Western blot using ACE2 antibody indicates that ACE2 protein levels are increased in the ileum of mice fed HFD for 12- and 48-wk compared with chow-fed mice. ACE2 protein levels in the colon did not differ between HFD- and chow-fed mice. (G,H) Quantification of Western blot intensities in (E,F) estimating the amount of ACE2 protein levels in the ileum. (I) Significantly higher ACE2 level in the ileum of mice fed an HFD for 48-wk by immunohistochemical analysis. (J) The surface ACE2-ir area percentage in each villi quantified by imaged J. Data are presented as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, †P <0.001, ‡P < 0.01, vs controls. ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ACE-ir, angiotensin-converting enzyme immunoreactive; DI, diet induced; HFD, high-fat diet.