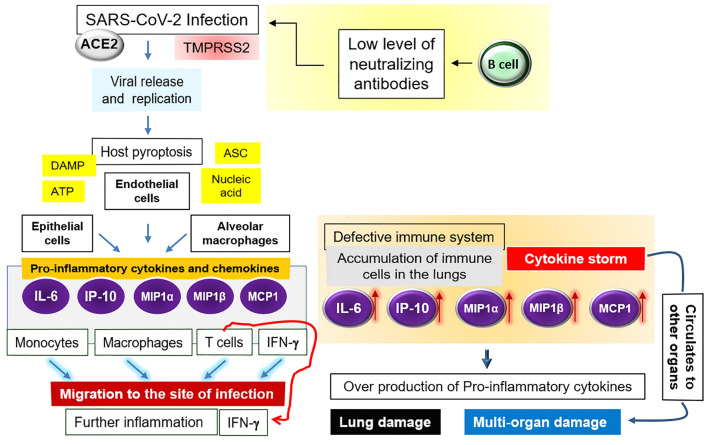
Fig. 1.
Immuno-pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2. Details are written in the text. Briefly, the SARS-CoV infection triggers the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (IL-6, IP-10, MIP1α), MIP1β and MCP-1) which attract monocytes, macrophages and T cells (in addition to the IFNγ) to the site of infection, promoting further inflammation. In case of defective immunity, the accumulation of immune cells in the lungs causes the overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn harms the lung and other organs. The non-neutralizing antibodies further facilitate the viral infection through ADE, and thereby fostering the organ damage