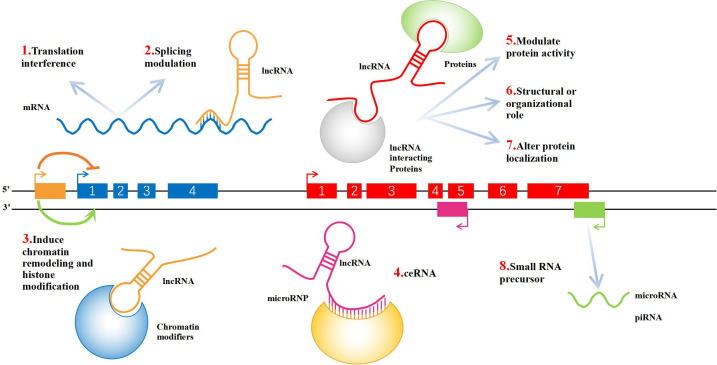
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) function. 1) LncRNA can be transcribed with the upstream promoter region of a protein-coding gene to interfere with the expression of downstream genes. 2) LncRNA can form complementary double strands with the transcript of a protein-coding gene, interfering with the splicing of messenger RNA (mRNA) and forming different forms of splicing. 3) LncRNA can mediate chromatin remodelling and histone modification, affecting the expression of downstream genes. 4) LncRNA has microRNA (miRNA) action sites, which can be competitively combined with miRNA. RNAs that act this way are known as miRNA sponges (competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs)). 5) In combination with specific proteins, lncRNA transcripts can regulate the activity of corresponding proteins. 6) As a structural component, it forms a nucleic acid–protein complex with protein. 7) LncRNA can bind to a specific protein, changing its cellular location. 8) LncRNA can form the precursor molecule of small RNAs (such as miRNA, PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA)).