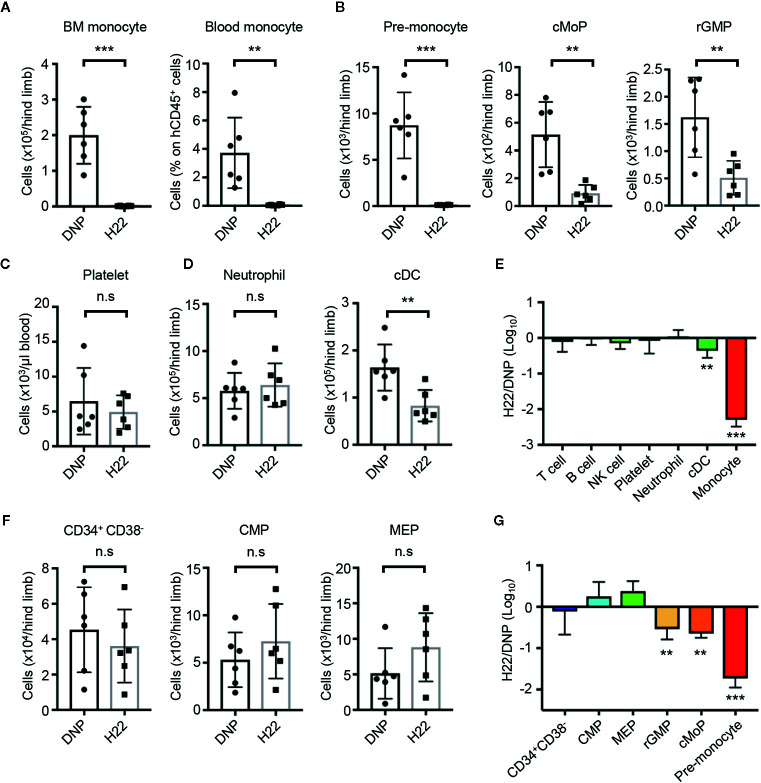
Figure 4.
H22-dPBD-mediated elimination of monocytes and their progenitors without severe side effects in hematopoiesis. (A–G) BM-humanized NOG mice were generated as shown schematically in Supplementary Figure 3 . Seven days after intravenous administration of DNP-dPBD or H22-dPBD (0.5 µg/mouse), hematopoietic cells in the BM and blood were analyzed by FCM. The number of BM monocytes and frequency of blood monocytes (A), cell numbers of monocytic progenitors in the BM (B), concentration of platelets (TER119-CD235ab-hCD41a+hCD41b+) in the blood (C), numbers of neutrophils and cDCs in the BM (D), and numbers of Lin-CD34+CD38- HSPCs, CMPs, and MEPs in the BM (F) are shown. Ratios in cell numbers of mature immune cells in the BM and results of their statistical analyses between DNP-dPBD- and H22-dPBD-treated mice are summarized in (E). Ratios in cell numbers of HSPCs and results of their statistical analyses between DNP-dPBD- and H22-dPBD-treated mice are summarized in (G). Each point in the bar graphs shows the value for an individual mouse (n=6 per group). Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean. Student’s t-test (A–D, F) was used to assess statistical significance. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; n.s, not significant. Data were pooled from two (C) or three (A, B, D, F) independent experiments.