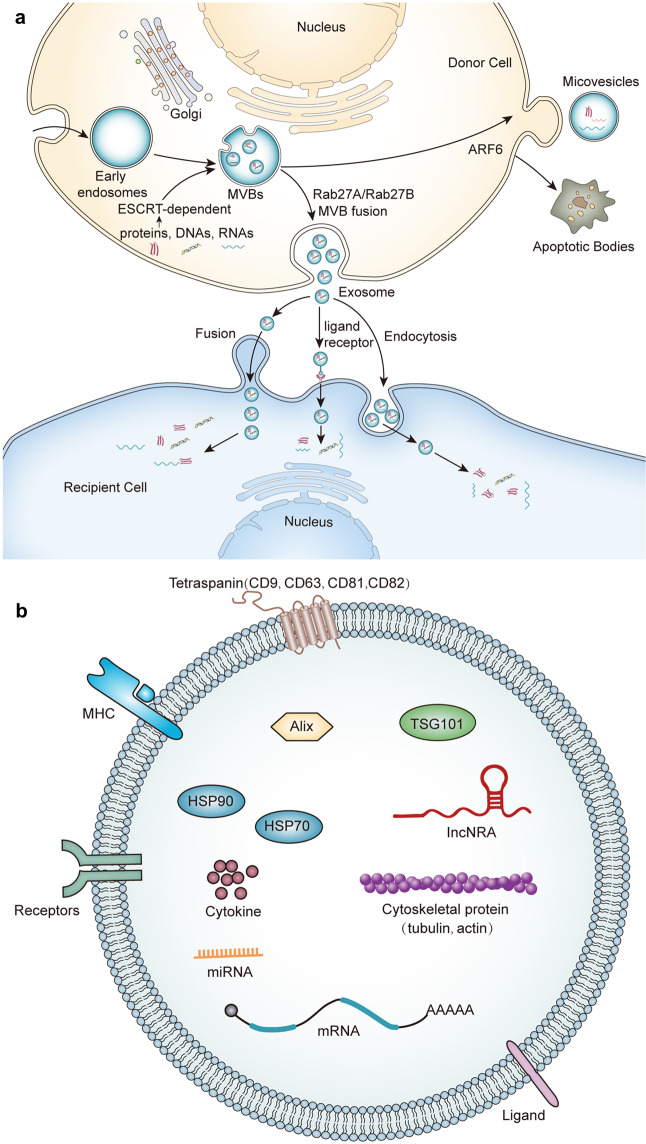
Fig. 2.
The classification, biogenesis, and content of EVs. a Exosomes originate from the reverse germination of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is recessed inward to form early endosomes, which are then sorted on the endoplasmic reticulum and processed on the Golgi apparatus to form multivesicular bodies. During this process, DNA, RNA, protein, and lipids in cells are sorted into vesicles mainly through ESCRT-dependent pathways. Under the regulation of the Rab family protein (Rab25/Rab27), MVBs fuses with the plasma membrane and are released into the extracellular space to form exosomes. Microvesicles are produced by outward germination and fission of the donor cell plasma membrane. GTP binding protein ARF6 of rho family members plays an important role in the formation of MVs. Few studies have reported the biogenesis of apoptotic bodies, which are currently considered to be relatively large vesicles derived from apoptotic cells. b EVs contain multiple types of cargoes, including nucleic acid, proteins, and liquids. EVs contain high levels of tetraspanins proteins (CD9, CD63, CD81, and CD82), MHC molecules, heat shock proteins (HSP 70 and HSP 90), and other transmembrane proteins and signal receptors