Fig. 1. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian mitochondrial dynamics.
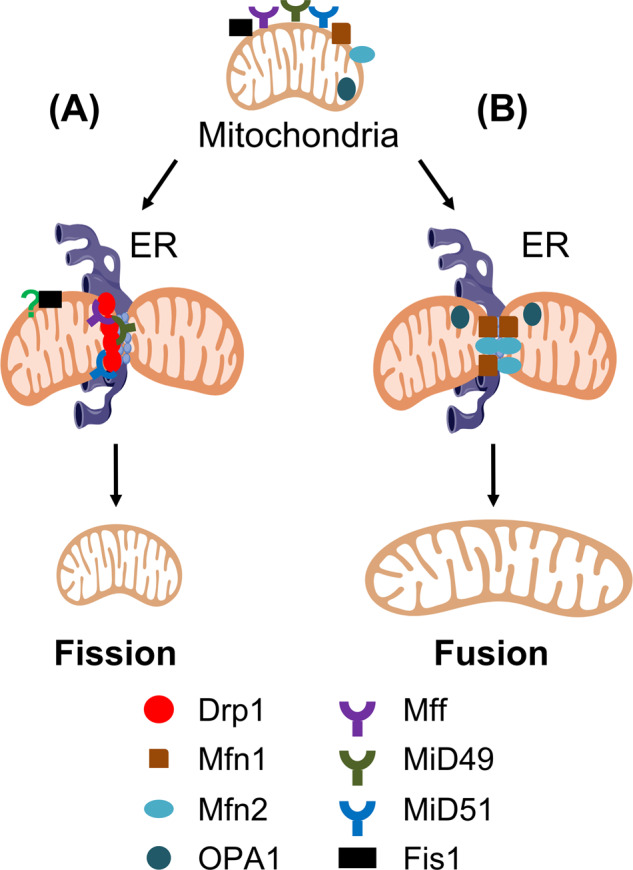
A During mitochondrial division, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) converges with mitochondria. At the constriction sites spatially marked by mitochondria-associated membranes (MAM), Drp1 is recruited by Mff, MiD49 or MiD51 onto the cytosolic surface of mitochondria and acts as a GTPase to complete the scission of outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM). Although Fis1 was originally identified as an essential Drp1 adapter for fission in yeast, it is dispensable for mitochondrial dynamics in mammals. B In contrast to fission, OMM proteins Mfn1 and Mfn2 form mitofusin complexes by homo-dimerization or hetero-dimerization to tether the adjacent outer membranes. Driven by mitofusin proteins GTPase activity, OMM first fuses, followed by the subsequent inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) fusion, due to the GTPase activity of OPA1.
