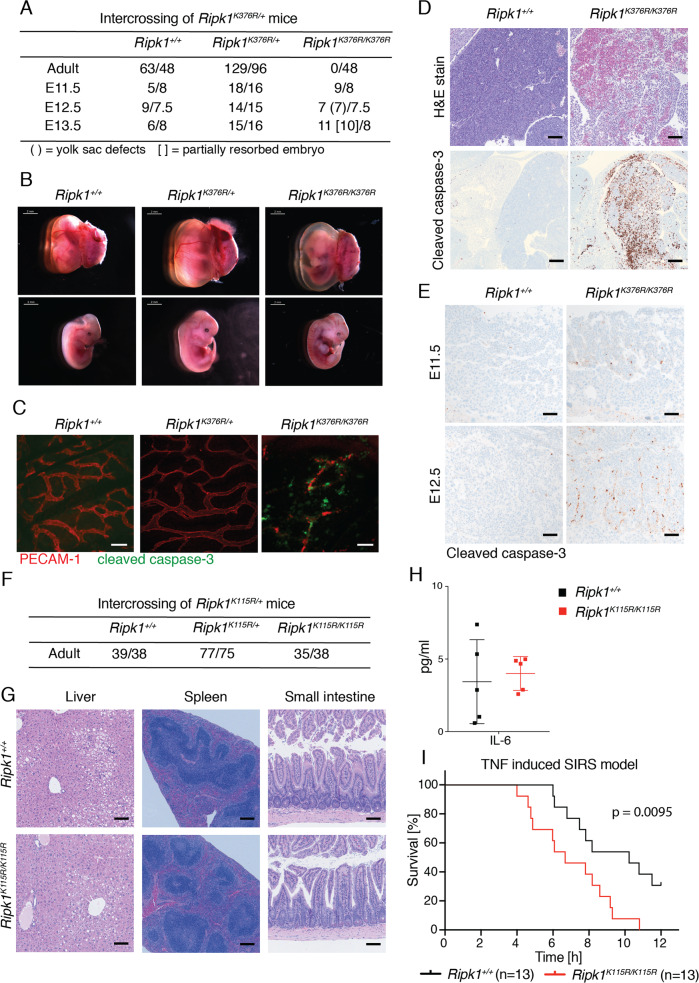
Fig. 1. RIPK1 K376R mutation cause embryonic lethality, while RIPK1 K115R mutation does not affect survival.
a Numbers of offspring at different embryonic days and adult age from intercrossing Ripk1K376R/+ mice. b Representative embryos of the Ripk1K376R/+ intercross at E12.5. Scale bars on the top left of each image indicate 2 mm. c Yolk sac of Ripk1+/+, Ripk1K376R/+ and Ripk1K376R/K376R intercross labeled for cleaved caspase-3 [green] and PECAM-1 [red] [scale bar 50 μm]. d Hematoxylin and eosin staining [upper panels, scale bar 100 μm] and IHC for cleaved caspase-3 [lower panels, scale bar 200 μm] of Ripk1+/+ and Ripk1K376R/K376R embryos. e IHC labeling for cleaved caspase-3 in the placenta labyrinths of Ripk1+/+ and Ripk1K376R/K376R embryos [scale bar 100 μm]. f Numbers of offspring from intercrossing Ripk1K115R/+ mice. g Histology of liver, spleen and small intestines of 12–15 months aged Ripk1+/+ and Ripk1K115R/K115R mice [scale bar 100 μm liver and small intestine, 200 μm spleen]. h Serum cytokine levels of IL-6 in Ripk1+/+ [n = 5] and Ripk1K115R/K115R [n = 5] 12–15 months old. i Survival of Ripk1+/+ in black [n = 13 males] and Ripk1K115R/K115R in red [n = 13 males] mice in TNF-induced SIRS model with 500 μg/kg TNF injected iv. Difference between the two groups by Mantel–Cox test: p = 0.0095.