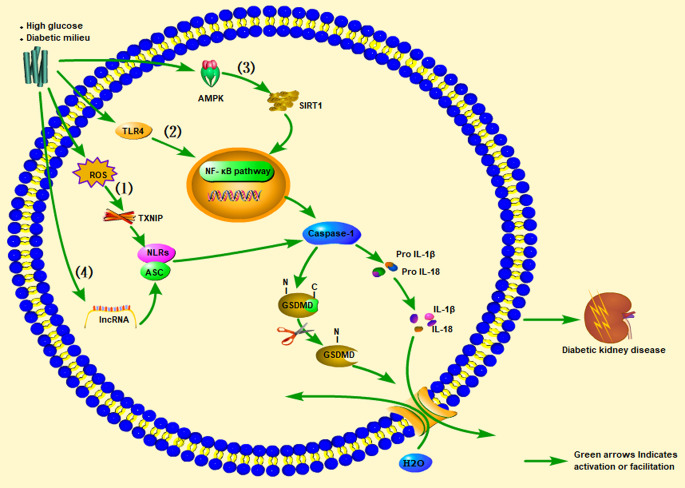
Figure 2.
Promotion of inflammasome pathways associated with pyroptosis of cells in the kidney (glomerular endothelial cells, tubular epithelial cells, podocytes, tubular epithelial cells) under high-sugar or diabetes conditions, leading to diabetic kidney disease (DKD). In renal cells stimulated by high glucose (HG): (1) ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway, (2) TLR4/NF-κB inflammasome signaling pathway, (3) AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB inflammasome signaling pathway, or (4) lncRNA)-related signaling pathways, they all activate pro-caspase-1 to become mature caspase-1. Caspase-1 cleaves GSDMD and activates the inactive pro IL-1β and pro-IL-18 to become mature IL-1β and IL-18, and the released GSDMD-NT forms a pore in the cell membrane, ultimately leading to DKD. ROS, Reactive oxygen species; TXNIP, Thioredoxin-interacting protein; AMPK, Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; SIRT1, Silent information regulation 2 homolog1; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-B.