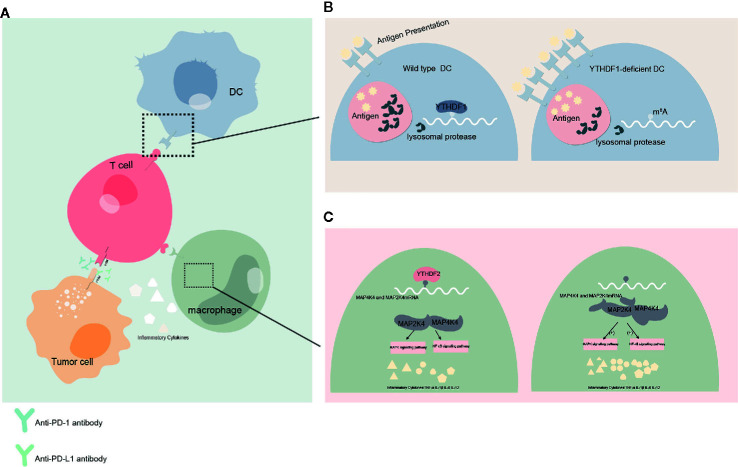
Figure 3.
Effect of YTHDFs on tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) (A) Dendritic cells (DC) presents the antigen to the surface of T cells and initiates the adaptive immune response. Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a negative immune checkpoint pathway that inhibit immune responses and promotes immune escape of tumor cells. This process can be blocked by anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies. Macrophages can affect anti-tumor immunity by secreting inflammatory factors. (B) When YTHDF1 is deficient, the translation efficiency of lysosomal protease transcripts decreases, the degradation of antigens is reduced, more antigens are involved in antigen presentation, and the immune response of T cells is enhanced. This process may affect the efficacy of PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors. (C) In macrophages, YTHDF2 knockdown promotes the translation and stability of MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 mRNA, which activates MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways and promotes the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These inflammatory factors can participate in the regulation of immune response and affect the efficacy of anti-tumor immunity.