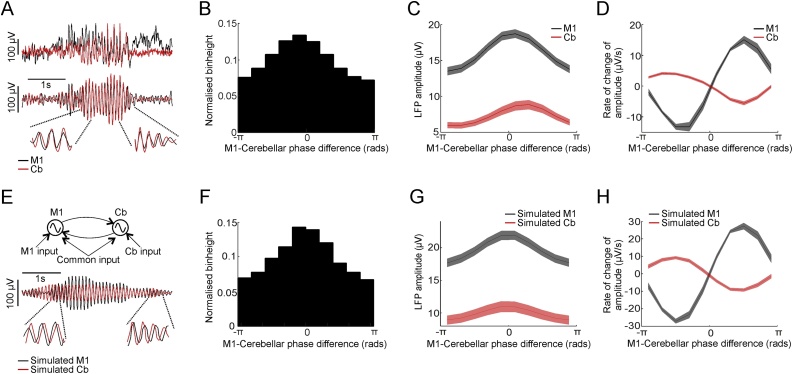
Fig. 8.
Phase relationship between M1 and Cerebellar spindles. A. Top: Example M1 (red) and cerebellar (black) spindles. Bottom: The same signals filtered between 7-15 Hz. B. Histogram of instantaneous phase differences between spindle-band M1 and cerebellar signals for example session. C. Mean amplitude of M1 and cerebellar spindle oscillations against their instantaneous phase difference (relative to preferred phase for each session). Shading indicates s.e.m. over all sessions with monkey U. D. Plot of mean amplitude derivative for M1 and cerebellar spindle oscillations against their instantaneous phase difference. E. Schematic of bidirectional coupling between spindle oscillators (top) and example model output (bottom). F—H. Same as BD— but for simulated M1 and cerebellar signals fit to each session in Monkey U. See Supplemental Fig. 6 for phase and phase derivative relations of all animals.