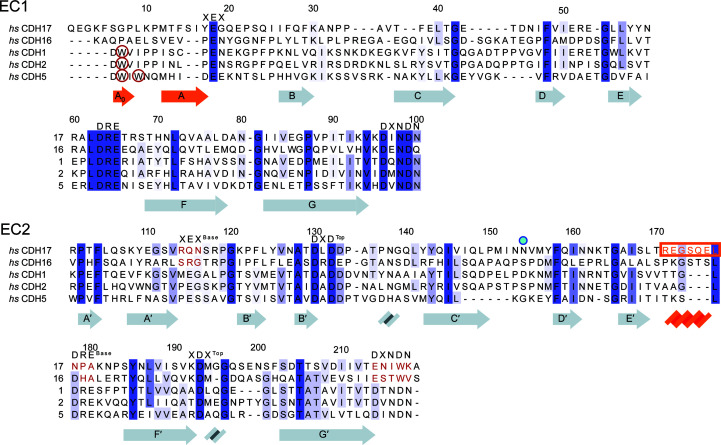
Figure 1.
Sequence similarity among CDH17, CDH16 and classical cadherins. Protein sequence alignments of the EC1 and EC2 repeats of the 7D-cadherins (CDH17 and CDH16) and three classical cadherins (CDH1, CDH2 and CDH5) show how these differ at their N-termini and at their EC2 C-terminal tails. Calcium-binding residues are highlighted with their respective sequences at the top. Missing calcium-binding motifs are highlighted in red for CDH17 and CDH16 in EC2. Tryptophan residues that classical cadherins utilize for the strand-swap mechanism are circled in red. The Asn154 residue implicated in disease is denoted by a blue dot (Smith et al., 2017 ▸). Secondary-structure elements of the hs CDH17 EC1–2 structure are highlighted below the sequence, with unique structural elements in orange. The sequence of the α-helix in CDH17 EC2 is highlighted by an orange box and text.