FIGURE 2.
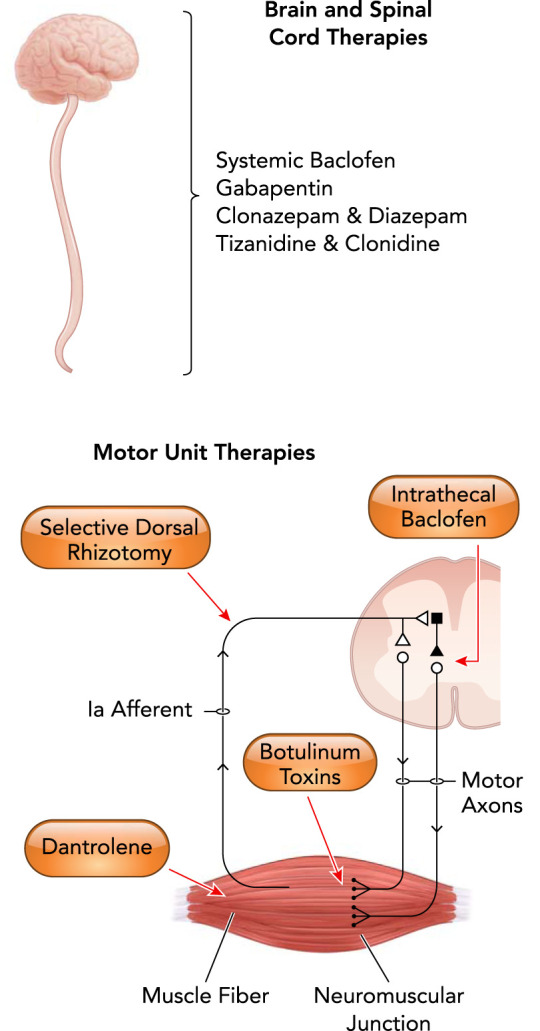
Medical and surgical interventions in the treatment of spastic cerebral palsy
All of the current clinical treatments for spastic CP involve both the brain and the spinal cord. Indeed, most treatments exclusively affect the spinal cord, motor neuron and/or motor unit alone. Treatment with baclofen, a presynaptic GABA agonist, may be orally (systemic) or intrathecally (targeting spinal cord neurons) administered. Gabapentin is a mild GABAmimetic and binds the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Clonazapam and diazepam are similar GABA receptor agonists. Tizanidine and clonidine primarily reduce interneuron activity within the spinal cord via agony of α2 adrenergic receptors. Selective dorsal rhizotomy selectively removes Ia afferent inputs to motor neurons, reducing their reflex excitability. Dantrolene works at the level of skeletal muscle, inhibiting the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
