FIGURE 6 – RBP complexes are affected in ALS models.
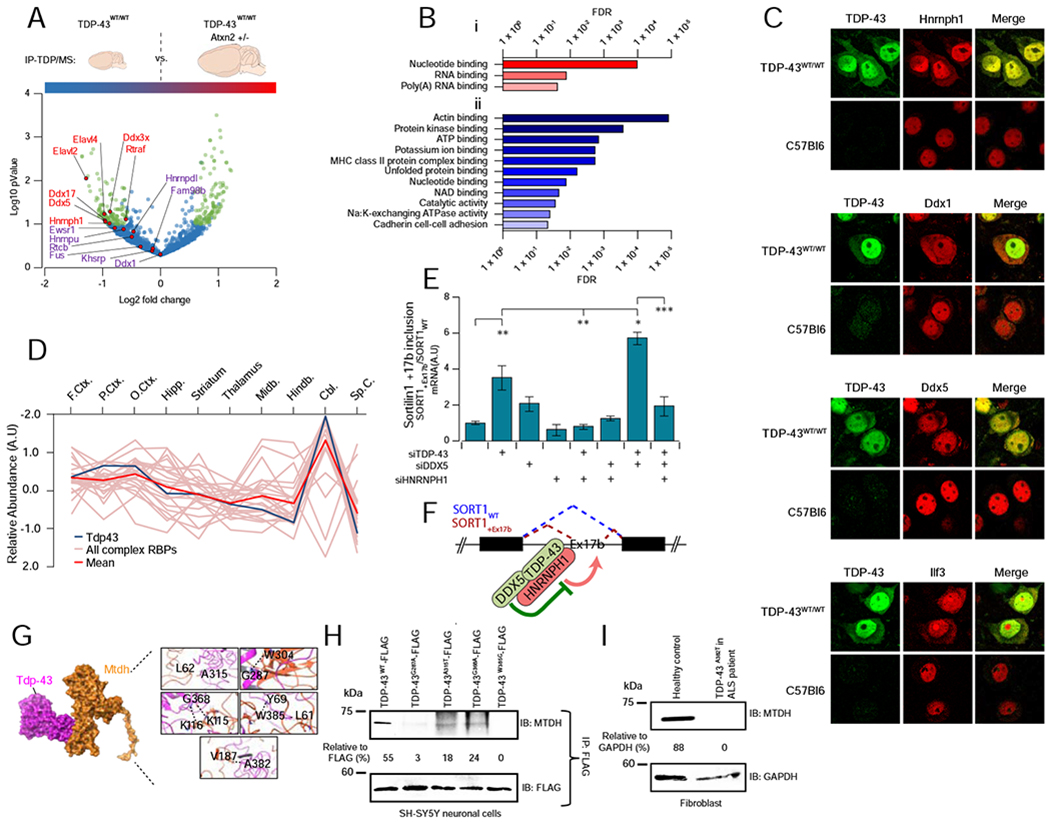
A Complex 22 is responsive to neuropathology. Volcano plot summarizing results from co-IP pulldowns of exogenous TDP-43 from cortical lysates from diseased (TDP-43WT/WT) versus protected (TDP-43WT/WTAtxn2[+/−]) transgenic mice. Precipitates were subject to quantitative mass spectrometry to define differential binding to pathogenic TDP-43 (> ±0.50x Log2-fold, −Log10 P < 1, highlighted in green). Interaction of Hnrnph1, Ddx5 and Ddx17 significantly reduced in protected animals (n = 4 per group, students t-test P ≤ 0.05).
B Gene ontology molecular function annotations of proteins showing (i) decreased interaction and (ii) increased interaction with transgenic TDP-43 in protected TDP-43WT/WTAtxn2[+/−] murine brain. Shown are terms with FDR−1 >20.
C Confocal immunofluorescent microscopy showing a redistribution of Complex 22 RBPs (Hnrnph1, Ddx1, Ddx5, Ilf3) into human TDP-43 positive cytoplasmic accumulations (arrows) in affected cortical neurons of transgenic TDP-43WT/WT mice, which is not seen in wild type animals. Scale bar = 20μm.
D The relative brain region expression pattern of Tardbp (TDP-43; dark blue line) closely mirrors the mean expression complex 22 expression (red line). Other RBP components are traced in pink.
E Knockdown (siRNA) of TDP-43 or TDP-43/DDX5 together results in the inclusion of Exon 17b of sortilin1 (SORT1) in SH-SY5Y cells (quantified by qPCR), whereas knockdown of interacting partner HNRNPH1 blocks this effect. Graphs show ratio (mean ± SEM) of SORT1 transcripts with/without exon17b (SORT1+Ex17b vs SORT1WT); n = 3 per group (ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison between all groups: * P < 0.05, ** P< 0.01, *** P < 0.001).
F Model of TDP-43 and DDX5 interaction illustrates coordinate inhibition of SORT1 Ex17b inclusion, dependent upon joint association with HNRNPH1.
G Structural model of mutations in residues of TDP-43 linked to familial ALS (A315T, G287A, G368A, W385G, A382T) that map to the interaction interface with MTDH.
H Co-IP analysis showing a reduced association of MTDH in SH-SY5Y cells expressing FLAG-tagged TDP-43 with ALS-relevant mutations at the predicted interaction interface.
I TDP-43 interaction with MTDH is abrogated in ALS-patient-derived fibroblasts carrying a pathogenic mutation (A382T), as compared to fibroblasts from a healthy control.
