Abstract
Introduction
Healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) are a worldwide problem. Infection control in hospitals is usually implemented by an infection control team (ICT). Initially, ICTs consisted of doctors, nurses, epidemiologists and microbiologists; then, in the 1980s, the infection control link nurse (ICLN) system was introduced. ICTs (with or without the ICLN system) work to ensure the health and well-being of patients and healthcare professionals in hospitals and other healthcare settings, such as acute care clinics, community health centres and care homes. No previous study has reported the effects of ICTs on HCAIs. This systematic review aims to assess the effectiveness of ICTs with or without the ICLN system in reducing HCAIs in hospitals and other healthcare settings.
Methods and analysis
We will perform a comprehensive literature search for randomised controlled trials in four databases: PubMed, Embase, CINAHL and the Cochrane Library. The primary outcomes are: patient-based/clinical outcomes (rate of HCAIs, death due to HCAIs and length of hospital stay) and staff-based/behavioural outcomes (compliance with infection control practices). The secondary outcomes include the costs to the healthcare system or patients due to extended lengths of stay. Following data extraction, we will assess the risk of bias by using the Cochrane Effective Practice and Organization of Care risk of bias tool. If data can be pooled across all the studies, we will perform a meta-analysis.
Ethics and dissemination
We will use publicly available data, and therefore, ethical approval is not required for this systematic review. The findings will be submitted for publication in peer-reviewed journals.
Trial registration number
CRD42020172173.
Keywords: infection control, health & safety, education & training (see medical education & training)
Strengths and limitations of this study.
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review of randomised controlled trials to assess the effects of infection control team implementation with or without the infection control link nurse system to reduce healthcare-associated infections in hospitals and other healthcare settings.
The comprehensive literature search, followed by a transparent and systematic study selection, data extraction and quality assessment by two review authors, will be the strength of this review.
The restriction of articles published in the English language may introduce publication and language bias, respectively.
There may be high heterogeneity due to complex intervention and different reporting standards for infection rates.
Introduction
Healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) are infections that patients acquire while they are receiving care for other illnesses at hospitals, acute care clinics, community health centres or care homes.1 A high proportion of HCAIs occur in the intensive care unit, and many HCAIs are due to the use of invasive devices, in particular, central lines, urinary catheters and ventilators.1 The true global burden of HCAIs remains unknown due to the lack of reliable data. However, the pooled HCAI prevalence has been reported to be 7.6% in high-income countries and 10.1% in low-income and middle-income countries.1 HCAIs are problematic for both patients and healthcare professionals as they result in prolonged hospital stays, increased resistance of micro-organisms to antimicrobial agents and additional financial burden for the health system and patients.1 2
The risk of HCAIs can be reduced by adhering to infection control guidelines.3 In healthcare setting, hand hygiene, the use of clean and well-functioning equipment and infection prevention and control programmes and teams are effective in preventing a large proportion of HCAIs.4 5 The WHO recommends having a dedicated and trained team in each acute healthcare facility to prevent HCAIs.4 Infection control in hospitals is implemented by the infection control team (ICT).6 ICTs originated in the UK in the 1950s and have been established in many countries.6 Initially, doctors, nurses, epidemiologists and microbiologists were trained as infection control specialists and appointed in the ICT.6 Later, infection control specialists were referred to by a variety of different titles, such as infection control professionals, infection control practitioners or infection preventionists.7–10 The majority of infection control specialists are nurses, known as infection control nurses (ICNs). Many countries apply a standard of one ICN per 250 hospital beds and one epidemiologist or medical microbiologist per 1000 hospital beds.11 Hospital epidemiologists are clinicians such as physicians or paediatricians with training in infection control.12
The roles of the ICT generally include: developing and executing infection control programmes, developing and disseminating guidelines, coordinating continuous education and training, establishing systems for surveillance of HCAIs (including outbreak detection), monitoring and auditing the practices and standards of care for infection control, facilitating access to the essential infrastructure, materials and equipments, building effective links with related programmes and promoting the implementation of multimodal strategies.13 14 The multifaceted roles of ICNs include: leading prevention activities such as infection surveillance, implementing evidence-based best practices and educating staff regarding these, conducting outbreak investigations, monitoring infection prevention compliance activities, reporting infection data to the public and governing agencies and observing organisational preparedness and responses to infectious diseases.15
In the late 1980s, the infection control link nurse (ICLN) system was first introduced due to limitations such as the limited engagement and overdependence on the ICT by the clinical staff, the lack of ownership of infection control in clinical wards and the challenge of recruiting qualified and experienced infection control professionals.16–18 The ICT system has since expanded to include new roles, such as ICLNs and infection control champions (ICCs). ICLNs and ICCs are ward-based staff who work under the supervision of ICNs16 and act as a link between their own clinical wards and the ICT.14
The roles of the ICLNs and ICCs include acting as a role model for infection control best practices for each ward, facilitating liaison between wards and the ICT, acting as a local resource for the ward for infection control issues, promoting and monitoring infection control practices at ward level, assisting in early detection of outbreaks, providing relevant infection control training, undertaking infection control audits and conducting research.16 18 19
Team-based healthcare and practices improve patient outcomes and the efficiency and quality of service, as well as reducing healthcare costs and increasing job satisfaction.14 20–22 Previous systematic reviews have reported that educational and bundled behavioural interventions are effective in preventing HCAIs.23 24 A scoping review qualitatively identified the working practices of ICTs but did not report their effectiveness or cost-effectiveness.14 Another scoping review reported the concept of the ICLN system but with limited evidence on the effectiveness of the ICLN system.19 In addition, a systematic review reported the facilitators for and barriers to the implementation of the ICLN system in acute healthcare settings.25 Therefore, the effectiveness of ICTs with or without the ICLN system in hospitals and other healthcare settings requires further investigation.
Review question
Is the ICT, with or without the ICLN system, effective in reducing HCAIs in hospitals and other healthcare settings?
Objective
The objective of this systematic review is to assess the effectiveness of ICTs, with or without ICLN systems in reducing HCAIs in hospitals and other healthcare settings.
Methods and analysis
This review protocol has been published in the PROSPERO International Prospective Register of systematic reviews (http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO), registration number: CRD42020172173 and follows the recommendations from the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols 2015 (PRISMA-P 2015) checklist (table 1).
Table 1.
PRISMA-P 2015 checklist
| Section and topic | Item no. | Checklist item | Information reported | Page number |
| Administrative information | ||||
| Title: | ||||
| Identification | 1a | Identify the report as a protocol of a systematic review. | Yes | 1 |
| Update | 1b | If the protocol is for an update of a previous systematic review, identify as such. | Not applicable | |
| Registration | 2 | If registered, provide the name of the registry (such as PROSPERO) and registration number. | Yes | 2, 4 |
| Authors: | ||||
| Contact | 3a | Provide name, institutional affiliation, email address of all protocol authors; provide physical mailing address of corresponding author. | Yes | 1 |
| Contributions | 3b | Describe contributions of protocol authors and identify the guarantor of the review. | Yes | 8 |
| Amendments | 4 | If the protocol represents an amendment of a previously completed or published protocol, identify as such and list changes; otherwise, state plan for documenting important protocol amendments. | Not applicable | |
| Support: | ||||
| Sources | 5a | Indicate sources of financial or other support for the review. | Not applicable | |
| Sponsor | 5b | Provide name for the review funder and/or sponsor. | Not applicable | |
| Role of sponsor or funder | 5c | Describe roles of funder(s), sponsor(s) and/or institution(s), if any, in developing the protocol. | Not applicable | |
| Introduction | ||||
| Rationale | 6 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known. | Yes | 4 |
| Objectives | 7 | Provide an explicit statement of the question(s) the review will address with reference to participants, interventions, comparators and outcomes (PICO). | Yes | 4 |
| Methods | ||||
| Eligibility criteria | 8 | Specify the study characteristics (such as PICO, study design, setting and time frame) and report characteristics (such as years considered, language and publication status) to be used as criteria for eligibility for the review. | Yes | 5–6 |
| Information sources | 9 | Describe all intended information sources (such as electronic databases, contact with study authors, trial registers or other grey literature sources) with planned dates of coverage. | Yes | 6 |
| Search strategy | 10 | Present draft of search strategy to be used for at least one electronic database, including planned limits, such that it could be repeated. | Yes | 6 and table 3 |
| Study records: | ||||
| Data management | 11a | Describe the mechanism(s) that will be used to manage records and data throughout the review. | Yes | 6–7 |
| Selection process | 11b | State the process that will be used for selecting studies (such as two independent reviewers) through each phase of the review (ie, screening, eligibility and inclusion in meta-analysis). | Yes | 6–7 |
| Data collection process | 11c | Describe planned method of extracting data from reports (such as piloting forms, done independently, in duplicate), any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators. | Yes | 6–7 |
| Data items | 12 | List and define all variables for which data will be sought (such as PICO items and funding sources), any preplanned data assumptions and simplifications. | Yes | 5–6 |
| Outcomes and prioritisation | 13 | List and define all outcomes for which data will be sought, including prioritisation of main and additional outcomes, with rationale. | Yes | 6 |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 14 | Describe anticipated methods for assessing risk of bias of individual studies, including whether this will be done at the outcome or study level, or both; state how this information will be used in data synthesis. | Yes | 7 |
| Data synthesis | 15a | Describe criteria under which study data will be quantitatively synthesised. | Yes | 7 |
| 15b | If data are appropriate for quantitative synthesis, describe planned summary measures, methods of handling data and methods of combining data from studies, including any planned exploration of consistency (such as I2, Kendall’s τ). | Yes | 7 | |
| 15c | Describe any proposed additional analyses (such as sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression). | Yes | 7 | |
| 15d | If quantitative synthesis is not appropriate, describe the type of summary planned. | Yes | 7 | |
| Meta-bias(es) | 16 | Specify any planned assessment of meta-bias(es) (such as publication bias across studies and selective reporting within studies). | Not applicable | |
| Confidence in cumulative evidence | 17 | Describe how the strength of the body of evidence will be assessed (such as GRADE). | Yes | 7 |
GRADE, grades of recommendations assessment, development and evaluation; PRISMA-P, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols.
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Studies
Inclusion criteria
In this review, we will include individual or cluster-randomised controlled trials. We will include studies conducted in hospitals or other healthcare settings, such as acute care clinics, community health centres and care homes, in any country.
Exclusion criteria
We will exclude interventional studies without control groups, observational studies and outbreak reports.
Participants
Inclusion criteria (Italicize this heading, please.)
All patients, regardless of age, in hospitals or other healthcare settings will be included as subjects in this review to examine the patient-based outcomes. In addition, this review will involve any kind of healthcare professional working in hospitals or other healthcare settings as subjects to examine their practices outcomes. These professionals may include doctors, nurses, epidemiologists, microbiologists and nursing care home staff.
Exclusion criteria (Italicize this heading please. Change the font size from medium to small, plase.)
We will exclude non-healthcare professionals, such as cleaning staff and healthcare professionals in non-clinical settings such as classrooms or learning laboratories.
Interventions and comparisons
Inclusion criteria (Italicize this heading, please.)
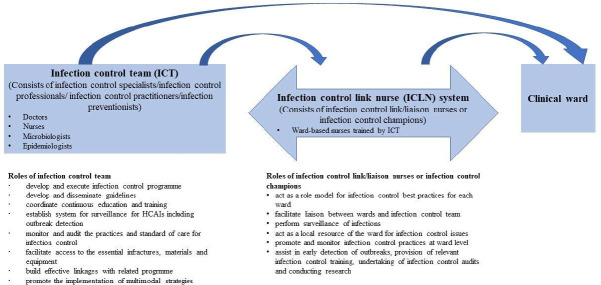
We will include any type of intervention that uses an ICT (with or without the ICLN system) intended to reduce HCAIs in hospitals or other healthcare settings. The intervention can be of any duration and frequency. We define ICT as a team made up of medical and nursing staff trained in certified infection prevention and control or its equivalent.13 Figure 1 summarises the members of the ICTs and their roles. We will include in this review if the ICT performs any of the following infection control measures:
Figure 1.
Members of ICTs and their roles in infection control.
Formulating and revising policies/guidelines.
Performing surveillance of HCAIs.
Training and educating healthcare professionals.
Monitoring and auditing practices and standard of care.
Liaising with other staff and departments.
Exclusion criteria (Italicize this heading please. Change the font size from medium to small, plase.)
We will exclude the infection control measures for HIV, tuberculosis and malaria because they are established as individual programmes and have stand-alone guidelines for infection control.
Comparison
We will include any other intervention or no intervention as comparison group.
Types of outcome measures
The primary outcomes of this review can be dividied into patient-based/clinical outcomes (rate of HCAIs, deaths due to HCAIs and length of hospital stays) and staff-based/behavioural outcomes (compliance with infection control practices as measured by study authors). The secondary outcomes include costs to the healthcare system or patients due to extended lengths of stays, if these are reported in the studies. For patient-based outcomes, we will pool the data from both prevalence and incidence studies and summarise them. The rate refers to the number of infection episodes or infected patients per 100 patients during the study period. We will not restrict the types of HCAIs or the timing of outcome assessment. The mortality will be calculated by dividing the number of deaths due to HCAIs by the total number of patients. Length of hospital stay will be presented in days. For staff-based outcomes, we will compare the proportion or frequency of compliance with infection control practices if the outcomes are binary data and calculate the mean difference if the outcomes are continuous data. We will include the costs to the healthcare system or patients due to extended lengths of stay and compare the mean or median differences between groups. A summary of the review eligibility criteria is presented in table 2.
Table 2.
Eligibility criteria
| Inclusion | Exclusion | |
| Population/setting | Patients in hospitals or other healthcare settings. Any kind of healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, epidemiologists, microbiologists and nursing care home staff. |
Non-healthcare professionals such as cleaning staff. Healthcare professionals in non-clinical setting such as class room or learning laboratory. |
| Intervention | All infection prevention and control measures by ICT with or without ICLN system such as:
The intervention can be of any duration and frequency. |
|
| Comparison | Any intervention or usual care. | |
| Outcome | Patient-based/clinical outcomes
Staff-based/behavioural outcomes 1. Compliance with infection control practices. Additional outcomes 1. Cost of healthcare system or patients. |
Hand hygiene compliance. Rate of antimicrobial prescription. |
| Study design | Randomised control trial (individual or cluster). |
|
| Period | No limitation. | |
| Language | English language only. |
HCAIs, healthcare-associated infections.
Search strategies
We will search four electronic databases for abstracts with full-text publications: PubMed, Embase, CINAHL and the Cochrane Library. We will not limit the publication date but will limit results to those in the English language. Related systematic reviews and primary studies will then be evaluated. A specific search strategy involving the use of Medical Subject Headings, Boolean operators, parentheses and truncation symbols will be applied. The PubMed search strategy is presented in table 3, and we will modify this as needed for use in other databases.
Table 3.
PubMed search strategy, modified as needed for use in other databases
| #1 | Search (“health personnel”(MeSH] OR health personnel(tw] OR (health* NEAR/3 personnel) OR “patient care team”(MeSH] OR patient care team*(tw] OR health care team*(tw] OR healthcare team*(tw] OR “physicians”(MeSH] OR “physician*“(tw] OR “doctor*“(tw] OR “nurses”(MeSH] OR “nurse*“(tw] OR link nurse*(tw] OR liaison nurse*(tw] OR “practitioner*“(tw] OR “specialist*“(tw] OR health consultant*(tw] OR healthcare professional*(tw] OR health care professional*(tw] OR “pharmacists”(MeSH] OR “pharmacist*“(tw] OR “microbiologist*“(tw] OR “champion*“(tw] OR “team*“(tw] OR manager*(tw] OR “preventionist*"(tw)) |
| #2 | Search (“infection control”(MeSH] OR infection control(tw] OR (infection* NEAR/3 control) OR (infection* AND control) OR infection prevention(tw] OR infection management(tw] OR (“infections”(MeSH] OR “infection*“(tw] AND (“control*“(tw] OR “prevention*“(tw] OR “management”(tw)))) |
| #3 | Search (infection control team*(tw] OR infection control specialist*(tw] OR “infection control practitioners”(MeSH] OR infection control practitioner*(tw] OR infection control doctor*(tw] OR infection control nurse*(tw] OR infection control link nurse*(tw] OR infection control champion*(tw] OR infection control preventionist*(tw)) |
| #4 | Search ((randomized controlled trial [pt] OR controlled clinical trial [pt] OR randomized [tiab] OR placebo [tiab] OR clinical trials as topic(mesh: noexp)OR randomly [tiab] OR trial [ti)) NOT (animals [mh] NOT humans [mh))) |
| #5 | Search (((#1 AND #2) OR #3) AND #4) |
| #6 | Search (((#1 AND #2) OR #3) AND #4) Filters: English |
Study selection and data extraction
Two review authors will perform initial screening of the titles and abstracts of primary studies from the output of searched databases using the online reference management software, Covidence (Covidence systematic review software, Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia. Available at www.covidence.org). Any disagreements will be resolved through discussion. Next, we will independently access the full text of potentially relevant studies and select the studies that meet the inclusion criteria. A standardised data extraction form will be prepared. We will pilot the form using at least one related study. This form will contain the following information: author (first author only), year of publication, study design, setting and country of the study, study duration, characteristics of participants, number of participants, details of intervention and control, types of outcome measures and study results. Discrepancies between the review authors will be resolved through consultation with all review authors. A study flow diagram (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses checklist) will be used to describe the number of studies identified, excluded and included in the review.
Risk of bias assessment in included studies
Two review authors will independently assess the risk of bias of each included study using the Cochrane Effective Practice and Organization of Care risk of bias tool.26 Disagreements will be discussed and resolved with reference to the main protocol and, when necessary, arbitration by the third review author.
Data analysis
We will present the characteristics of the included studies in a summary table. We will conduct a meta-analysis if we find two or more eligible studies where the participants, interventions, comparisons and outcomes are similar enough for pooling. We will use the I2 statistic to measure the heterogeneity among the included studies and interpret the results in accordance with the definitions in the Cochrane Handbook for the Systematic Reviews of Interventions.27 We will use random-effect meta-analysis as we may find heterogeneity due to complex interventions.28 We will use the risk ratio for dichotomous data and the mean differences for continuous data with corresponding 95% CIs. However, if there is an insufficient number of studies for data to be pooled, we will present the findings in a narrative manner. If the necessary data are available, we will perform subgroup analysis by categories of intervention (formulating and revising policies/guidelines, performing surveillance of HCAIs, training and educating healthcare professionals, monitoring and auditing practices and standard of care and liaising with other staff and departments) or by type of healthcare facilities (hospital, nursing homes or others). We will perform sensitivity analysis on primary outcomes by excluding trials with a high risk of selection bias. We will use the grades of recommendations assessment, development and evaluation approach to assess the certainty of evidence (very low, low, moderate and high) for the effectiveness of ICTs.
Patient and public involvement
We will not involve the patient or the public in this systematic review.
Ethics and dissemination
We will use publicly available data, and therefore ethical approval is not required for this systematic review. Our systematic review will provide evidence of whether ICT interventions can be effective in reducing HCAIs in hospitals and other healthcare settings. The findings will be disseminated at national and international conferences. In addition, this study will be submitted for publication in peer-reviewed journals. We expect that the relevance of the findings will be transferred to routine medical practice in hospitals and other healthcare settings after scientific evidence-based publication.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the critical input and support of the technical staff from the Bureau of International Health Cooperation, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Japan.
Footnotes
Contributors: MMT, SM, EO and TB conceived the idea, planned and designed the study protocol. MMT, SM, OR and TB contributed to search strategy and study selection criteria. MMT wrote the first draft. All authors reviewed, revised and approved the final version of the protocol for publication.
Funding: This work was supported by the National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Japan (19A10).
Disclaimer: The funding body played no role in developing the study nor in writing the manuscript.
Competing interests: The institution that employs MMT, SM and TB is due to receive funding from NIPRO pharmaceuticals (manufacturer of generic antimicrobial interventions) for consultation for tuberculosis diagnostic development. None of the authors of this review were involved in the consultation. The authors have not and will not benefit financially directly or indirectly from the funds. None of the authors have access to or control of NIPRO funds. The employer of MMT, SM and TB also received a fee from Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) to provide trainings on antimicrobial resistance in low-income and middle-income countries. NIPRO and JICA have had no input into the design of the protocol or this research.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.WHO . Report on the burden of endemic health care-associated infection worldwide. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Graves N, Weinhold D, Tong E, et al. Effect of healthcare-acquired infection on length of hospital stay and cost. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2007;28:280–92. 10.1086/512642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Flodgren G, Conterno LO, Mayhew A, et al. Interventions to improve professional adherence to guidelines for prevention of device-related infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;3:CD006559. 10.1002/14651858.CD006559.pub2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.WHO . Guidelines on core components of infection prevention and control programmes at the National and acute health care facility level. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.WHO . How to prevent sepsis. In: communities IHtps-trycpihca, ed. save lives: clean your hands 5 may 2018: World Health organization. Geneva: WHO, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jenner EA, Wilson JA. Educating the infection control team - past, present and future. A British prespective. J Hosp Infect 2000;46:96–105. 10.1053/jhin.2000.0822 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hall L, Halton K, Macbeth D, et al. Roles, responsibilities and scope of practice: describing the ‘state of play’ for infection control professionals in Australia and New Zealand. Healthc Infect 2015;20:29–35. 10.1071/HI14037 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Friedman C, Curchoe R, Foster M, et al. APIC/CHICA-Canada infection prevention, control, and epidemiology: professional and practice standards. Am J Infect Control 2008;36:385–9. 10.1016/j.ajic.2008.04.246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Crist K, Murphy D, Wright M-O, et al. The role of the infection preventionist in a transformed healthcare system: Meeting healthcare needs in the 21st century. Am J Infect Control 2019;47:352–7. 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.MacBeth D, Hall L, Halton K, et al. Credentialing of Australian and New Zealand infection control professionals: an exploratory study. Am J Infect Control 2016;44:886–91. 10.1016/j.ajic.2016.01.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haley RW, Culver DH, White JW, et al. The efficacy of infection surveillance and control programs in preventing nosocomial infections in US hospitals. Am J Epidemiol 1985;121:182–205. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Scheckler WE, Brimhall D, Buck AS, et al. Requirements for infrastructure and essential activities of infection control and epidemiology in hospitals: a consensus panel report. Society for healthcare epidemiology of America. Am J Infect Control 1998;26:47–60. 10.1016/s0196-6553(98)70061-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.WHO . Improving infection prevention and control at the health facility: interim practical manual supporting implementation of the who guidelines on core components of infection prevention and control programmes. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hale R, Powell T, Drey NS, et al. Working practices and success of infection prevention and control teams: a scoping study. J Hosp Infect 2015;89:77–81. 10.1016/j.jhin.2014.10.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Murphy DM, Hanchett M, Olmsted RN, et al. Competency in infection prevention: a conceptual approach to guide current and future practice. Am J Infect Control 2012;40:296–303. 10.1016/j.ajic.2012.03.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dawson SJ. The role of the infection control link nurse. J Hosp Infect 2003;54:251–7. 10.1016/S0195-6701(03)00131-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lewis T, Edwards C. How clinical champions can improve quality. Nurs Manag 2008;14:24–7. 10.7748/nm2008.03.14.10.24.c6492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lloyd-Smith E, Curtin J, Gilbart W, et al. Qualitative evaluation and economic estimates of an infection control champions program. Am J Infect Control 2014;42:1303–7. 10.1016/j.ajic.2014.08.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dekker M, Jongerden IP, van Mansfeld R, et al. Infection control link nurses in acute care hospitals: a scoping review. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2019;8:20. 10.1186/s13756-019-0476-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.van Weel C. Teamwork. The Lancet 1994;344:1276–9. 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)90756-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schmitt MH. Collaboration improves the quality of care: methodological challenges and evidence from US health care research. J Interprof Care 2001;15:47–66. 10.1080/13561820020022873 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Reeves S, Lewin S. Interprofessional collaboration in the hospital: strategies and meanings. J Health Serv Res Policy 2004;9:218–25. 10.1258/1355819042250140 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Safdar N, Abad C. Educational interventions for prevention of healthcare-associated infection: a systematic review. Crit Care Med 2008;36:933–40. 10.1097/CCM.0B013E318165FAF3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Aboelela SW, Stone PW, Larson EL. Effectiveness of bundled behavioural interventions to control healthcare-associated infections: a systematic review of the literature. J Hosp Infect 2007;66:101–8. 10.1016/j.jhin.2006.10.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Peter D, Meng M, Kugler C, et al. Strategies to promote infection prevention and control in acute care hospitals with the help of infection control link nurses: a systematic literature review. Am J Infect Control 2018;46:207–16. 10.1016/j.ajic.2017.07.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, et al. Rob 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019;2:l4898. 10.1136/bmj.l4898 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Higgins JPT TJ, Chandler J, Cumpston M, et al., . Cochane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.0 [updated July 2019]. London: Cochrane, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tanner-Smith EE, Grant S. Meta-Analysis of complex interventions. Annu Rev Public Health 2018;39:135–51. 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040617-014112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.