Figure 3.
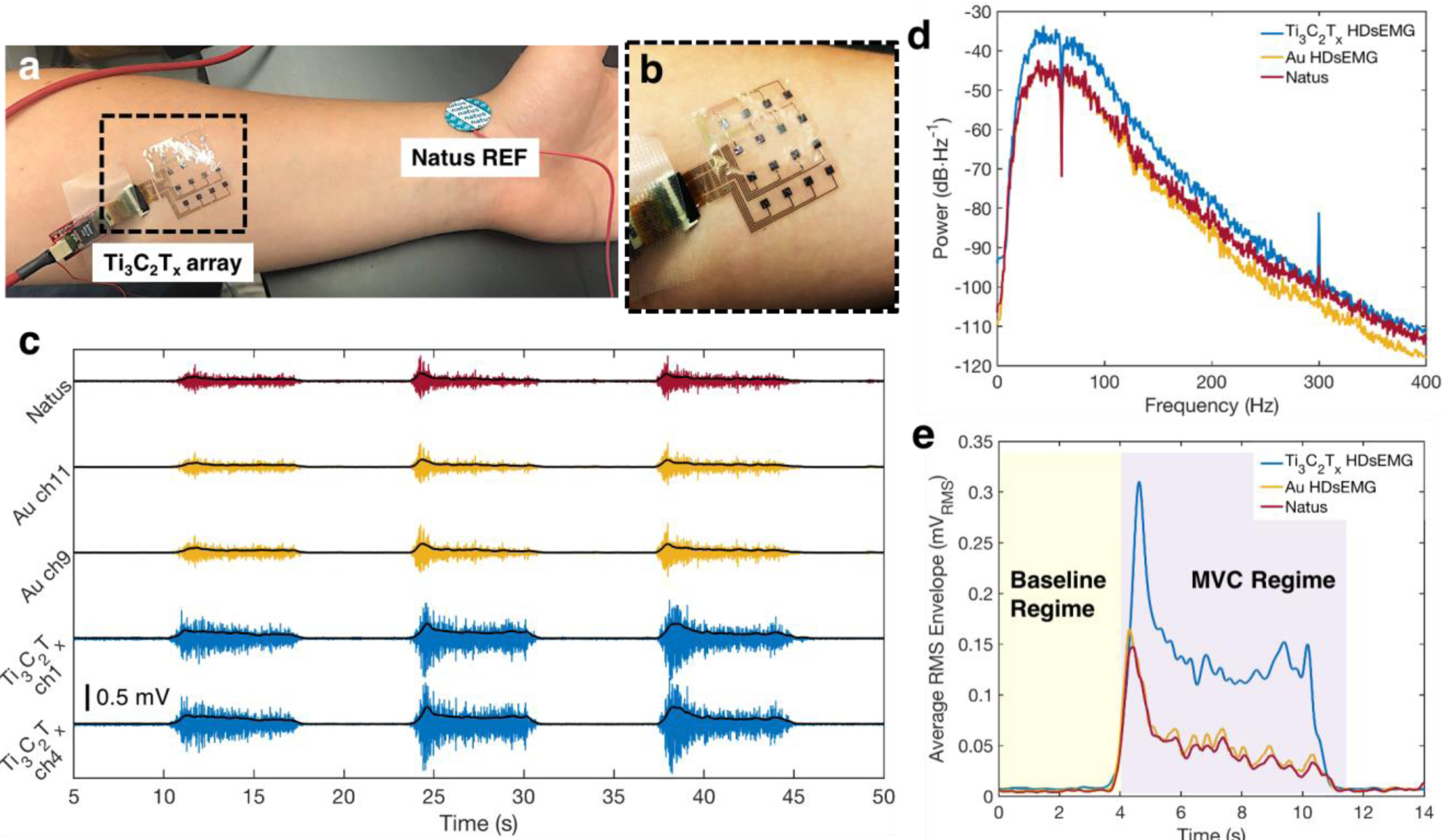
Baseline sEMG recordings with the Ti3C2Tx and HDsEMG arrays, and a Natus monopolar contact. a) Experimental setup for a standard voluntary contraction recording experiment. The Ti3C2Tx array is placed over the flexor digitorum superficialis, while Natus electrodes are placed on the elbow (not shown) and at the wrist, as ground and reference, respectively. b) Close-up image of the Ti3C2Tx array, showing its excellent skin conformability. c) Examples of the sEMG signal recorded from the FDS during a typical voluntary contraction experiment on two channels from the Ti3C2Tx and Au HDsEMG arrays, and a single Natus contact, for one subject. The RMS envelope of the sEMG signal is overlaid in black for each trace. Signals were recorded separately for the Ti3C2Tx array and the Au and Natus electrodes, but data was time- and amplitude-matched offline, for ease of viewing. d) Average power spectral density of the baseline sEMG recordings on all channels of the Ti3C2Tx and Au arrays, and a single Natus contact, for one subject. Note that a 60 Hz notch filter was applied to the data for all contacts. e) The average RMS envelope of the sEMG signal during the first contractions shown in (c), comparing the magnitudes of the RMS signals recorded on each of the three electrode types. A value was computed for the SNR for each electrode, using RMS values in the Baseline and MVC Regimes shaded in yellow and purple, respectively.
