Figure 6.
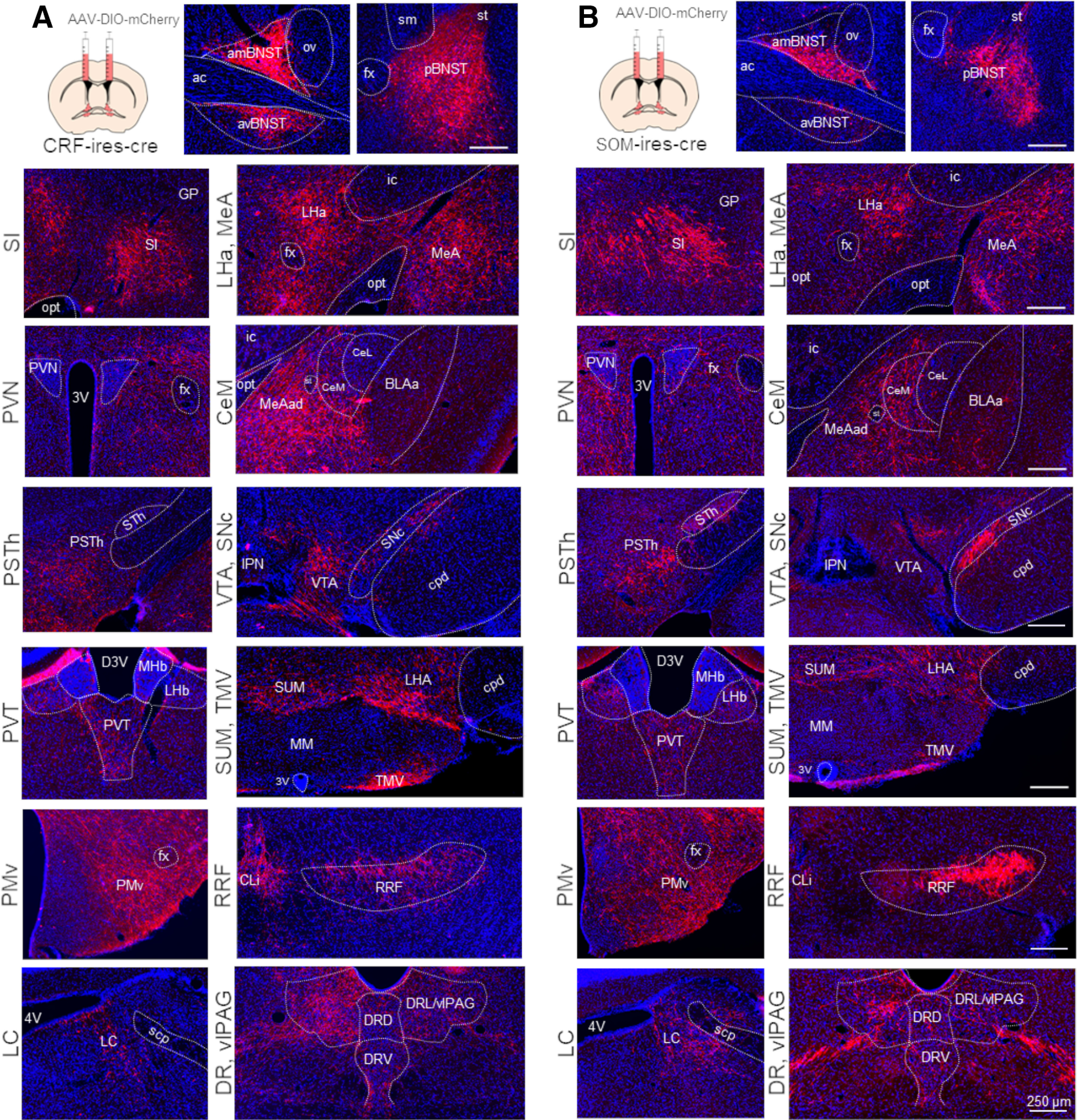
AAV based mapping of major projection areas of BNSTCRF (A) and BNSTSOM (B) neurons. Representative wide-field fluorescence photomicrographs show a highly similar distribution of BNSTCRF and BNSTSOM projections. 3V, third ventricle; 4V, fourth ventricle; ac, anterior commissure; amBNST, anteromedial BNST; avBNST, anteroventral BNST; BLAa, basolateral amygdala, anterior part; CeL, central amygdala, lateral part; CeM, central amygdala, medial part; CLi, central linear nucleus raphe; cpd, cerebral peduncle; D3V, dorsal part of the third ventricle; DRD, dorsal raphe, dorsal part; DRL, dorsal raphe, lateral part; DRV, dorsal raphe, ventral part; fx, fornix; GP, globus pallidus; ic, internal capsule; IPN, interpeduncular nucleus; LC, locus coeruleus; LHa, lateral hypothalamic area; LHb, lateral habenula; MeA, medial amygdala; MeAad, medial amygdala nucleus, anterodorsal part; MHb, medial habenula; MM, medial mammillary nucleus; opt, optic tract; ov, oval nucleus of the BNST; pBNST, posterior BNST; PMv, ventral premammillary nucleus; PSTh, parasubthalamic nucleus; PVN, paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus; PVT, paraventricular thalamic nucleus; RRF, retrorubral field; scp, superior cerebellar peduncles; SI, substantia innominate; sm, stria medullaris; SNc, substantia nigra, pars compacta; st, stria terminalis; STh, subthalamic nucleus; SUM, supramammillary nucleus; TMV, tuberomammillary nucleus, ventral part; vlPAG, ventrolateral periaqueductal gray; VTA, ventral tegmental area.
