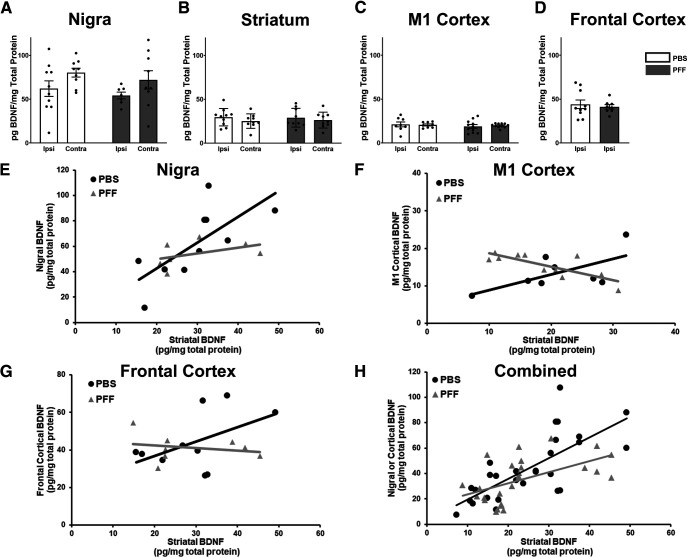
Figure 6.
α-Syn inclusions alter nigrostriatal and corticostriatal BDNF relationships. Total BDNF protein levels measured in the SN (A), striatum (B), M1 cortex (C), or frontal cortex (D) ipsilateral to injection revealed no differences (p > 0.05) because of pSyn inclusions. E, PBS-injected rats display a significant positive association between striatal and nigral BDNF protein levels (β = 2.02, SE = 0.58, p = 0.004) that is disrupted by treatment with PFFs, as reflected by the negative interaction term, however, is not significant (β = −0.90, SE = 0.56, p = 0.13). F, In the M1 cortex, PBS rats show a significant positive association with striatal BDNF (β = 0.98, SE = 0.40, p = 0.03) that is significantly disrupted by PFFs (β = −2.67, SE = 0.68, p = 0.001). G, The relationship between frontal cortical and striatal BDNF protein is positive, but not significant, in PBS-treated rats (β = 0.76, SE = 0.40, p = 0.08), and is disrupted, but not significant in PFF-treated rats (β = −1.58, SE = 0.91, p = 0.11). H, When all structures are combined, there is a significant positive association between source (nigra/cortex) and striatal BDNF protein levels (β = 1.08, SE = 0.26, p = 0.0001) that is significantly disrupted by PFF treatment (β = −0.835, SE = 0.33, p = 0.02). Values represent the mean ± SEM.