Figure 2.
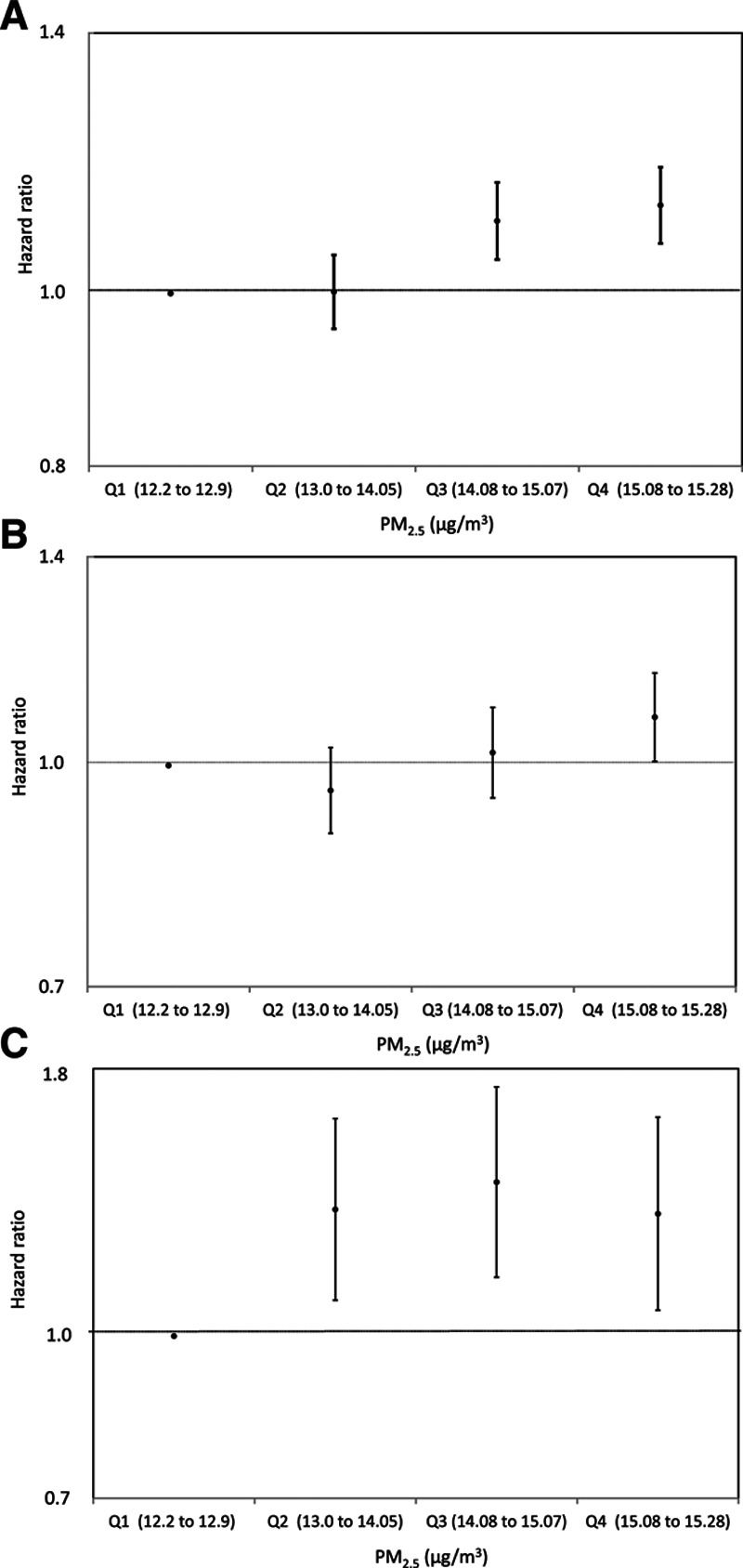
HRs for the association of quartile fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure and (A) natural-cause, (B) cardiorespiratory disease, and (C) lung cancer mortality. Error bars denote the 95% CIs.

HRs for the association of quartile fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure and (A) natural-cause, (B) cardiorespiratory disease, and (C) lung cancer mortality. Error bars denote the 95% CIs.