Figure 2.
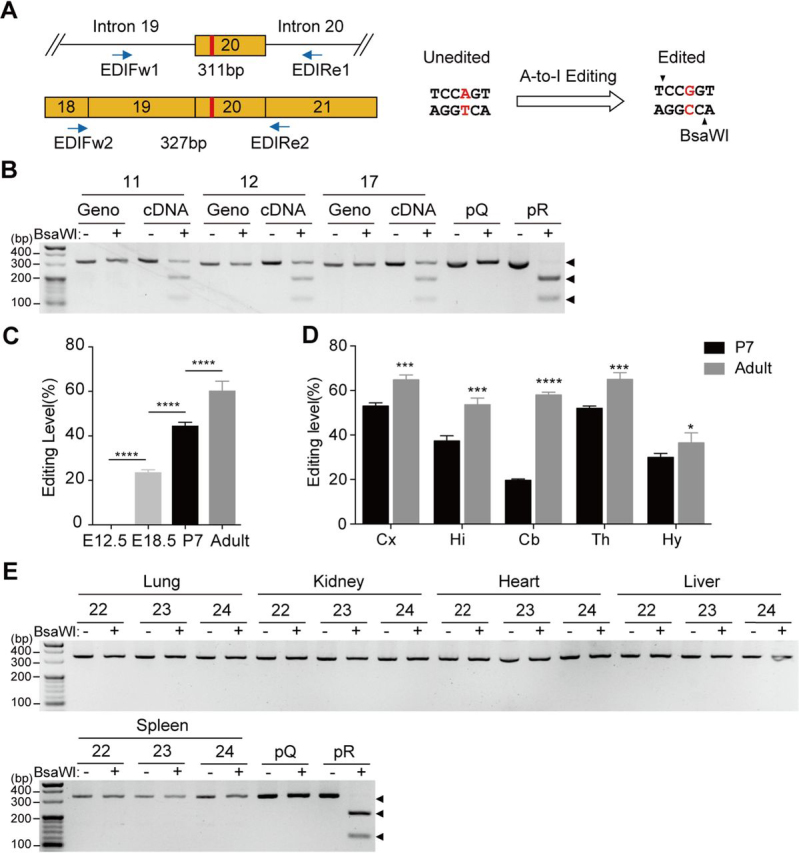
The brain-specific Q/R editing of Tmem63b varies with brain regions and ages.A, schematic demonstration of genomic (upper panel) and cDNA (lower panel) sequence around Tmem63b exon 20 with Q/R editing site marked in red. Primers for amplification are indicated. Q/R editing led to a BsaWI endonuclease recognizing site (right panel). B, Q/R editing of Tmem63b in brains of three adult mice with codes labeled above. The amplified sequences with unedited (Q) and edited (R) forms were indicated by black arrowheads. Plasmids with Q-form (pQ) and R-form (pR) Tmem63b cDNAs served as control to indicate the enzymatic activity of BsaWI. C, quantification of Q/R editing levels in brains of E12.5 (0.0 ± 0.0%, n = 3), E18.5 (23.7 ± 1.2%, n = 3), P7 (44.6 ± 1.5%, n = 5), and adult (60.3 ± 4.2%; n = 6) mice. Data are shown as mean ± S.D. (error bars). ****p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post hoc test. D, quantification of Q/R editing levels in cerebral cortex (Cx), hippocampus (Hi), cerebellum (Cb), thalamus (Th), and hypothalamus (Hy) of P7 (black column) and adult (gray column) mice. Data are shown in Table S1 as mean ± S.D. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; Student's t test, two-tailed. E, Q/R editing of Tmem63b was absent in lungs, kidneys, hearts, livers, and spleens from three adult mice with codes labeled above.
