Figure 10.
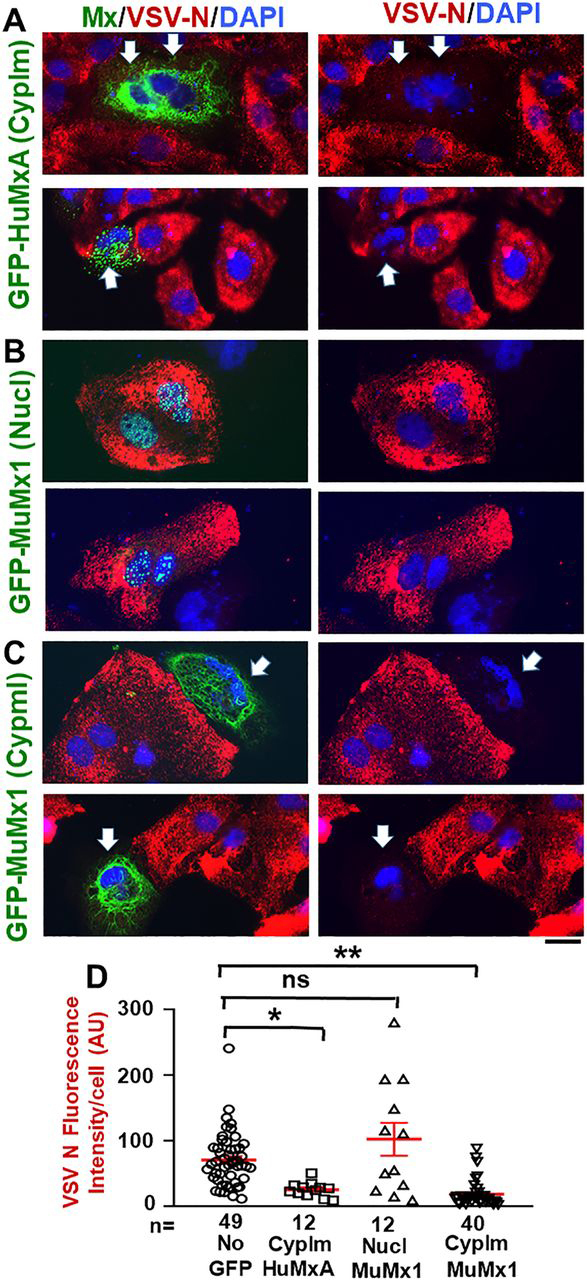
Antiviral phenotype of Huh7 cells with nuclear or cytoplasmic GFP-MuMx1 toward VSV. Huh7 cells (∼2 × 105 cells/35-mm plate), transfected with the GFP-HuMxA or GFP-MuMx1 expression vectors 2 days earlier, were replenished with 0.25 ml of serum-free Eagle's medium and then 20 µl of a concentrated VSV stock of the WT Orsay strain added (corresponding to multiplicity of infection >10 pfu/cell). The plates were rocked every 15 min for 1 h followed by the addition of 1 ml of full culture medium. The cultures were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 4 h after the start of the VSV infection, and the extent of VSV N protein expression in individual cells was evaluated using immunofluorescence methods (using the mouse anti-N mAb) and Image J for quantitation (33). A–C, representative cells showing the absence of any GFP or the appearance of cytoplasmic GFP-HuMxA, nuclear GFP-MuMx1, or cytoplasmic GFP-MuMx1 and the corresponding level of expression of viral N protein (thick arrows point to cells displaying an antiviral effect). All scale bars, 20 μm. D enumerates N protein expression in various classes of cells shown in A–C imaged at identical exposure settings and expressed in AU/cell. n, number of cells evaluated per group in this experiment (for this evaluation, cells with only cytoplasmic Mx1 were combined with cells with both cytoplasmic and nuclear Mx1); horizontal red lines within each group indicate mean ± S.E. (error bars). Statistical significance was evaluated using ANOVA (Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn's post-test for multiple comparisons); *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001; ns, not significant (p > 0.05).
