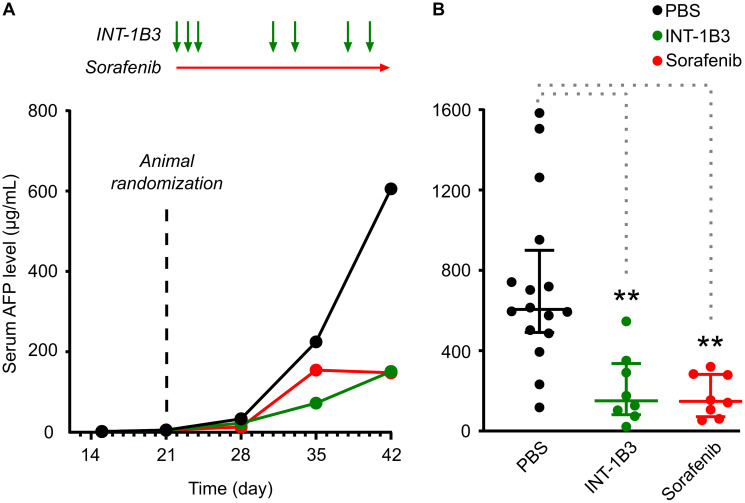
Figure 5. Effect of INT-1B3 on orthotopic human HCC Hep3B tumor growth in immune-compromised mice.
Human HCC Hep3B tumor fragments were implanted into the left liver lobe of SCID/Beige mice (orthotopic tumor model), as indicated in the Materials and Methods section. Serum AFP levels were measured as indicator of liver tumor development. On day 21, animals were randomized in experimental groups based on increasing serum AFP levels (median = 5.2 μg/mL), and treatment with test items started one day after (i.e., on Day 22). Animals were treated with either vehicle (PBS, i.p.; black) or INT-1B3 (10 mg/kg/administration, i.v.; green) daily for three days during the first week, then twice weekly for the following two weeks. Animals were also treated with sorafenib (10 mg/kg/administration, p.o., BID; red) as reference control in this experimental tumor model. Serum AFP levels were determined weekly throughout the study. (A) Time-dependent evolution of serum AFP levels (median, expressed as μg/mL). See Supplementary Figure 12 for a semi-log scale representation of the ~3 order of magnitude increase in AFP levels throughout the study. (B) on Day 42, serum AFP values from individual animals, median (horizontal bar), and interquartile range (vertical error bar) are presented on linear scale for the indicated experimental groups. ** indicates p-value < 0.01 by the 2-tailed non-parametric Mann–Whitney statistical analysis (p values of 0.005 and 0.002 for INT-1B3 (n = 8) and sorafenib (n = 8), respectively) as compared to PBS-treated group (n = 16).