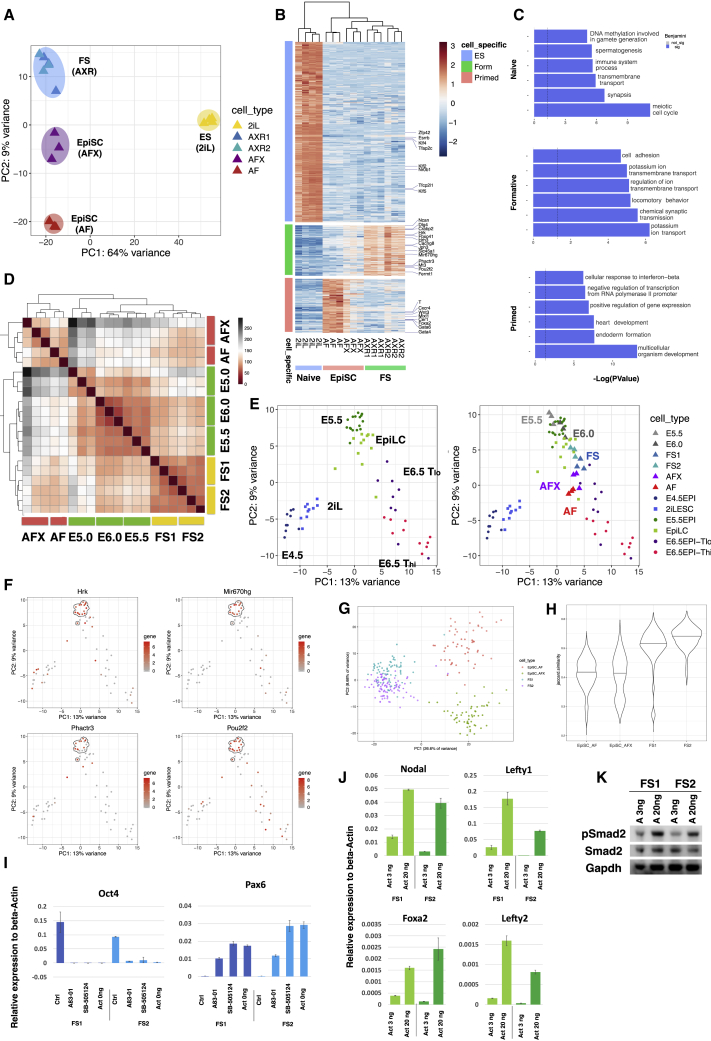
Figure 4.
Whole-Transcriptome Analysis and Nodal/Activin Pathway Activity
(A) PCA with all genes for ESCs, FS cells, and EpiSCs (AFX and AF).
(B) Heatmap clustering of naive, formative, and primed enriched genes.
(C) GO term analyses based on the genes identified in (B). x axis is −Log(p value). Top 6 significant terms are shown (Benjamini value, <0.05).
(D) Heatmap comparison of FS cells and AFX and AF EpiSCs with E5.0, E5.5, and E6.0 epiblast cells.
(E) Left, PCA with mouse single-cell data from embryos and EpiLCs (Nakamura et al., 2016). Right, samples from (D) were projected onto the single-cell PCA.
(F) Gene expression patterns of selected FS cell enriched genes identified in (B) colored on PCA from (E). E5.5 epiblast cells are highlighted by the dashed circle.
(G) PCA using 2,000 most abundant genes of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data from two FS cell lines and one AFX and one AF EpiSC line.
(H) Violin plot of Jaccard index analysis of 2,000 most abundant genes shows higher correlation between FS cells than EpiSCs.
(I) qRT-PCR analysis of FS cells in AloXR (Ctrl), with addition of 1 μM A83-01 or 5 μM SB5124, or withdrawal of activin for 2 days. Relative expression to beta-actin. Error bars are SD from technical duplicates.
(J) qRT-PCR analysis of FS cells cultured in low (3 ng/ml) and high (20 ng/ml) activin for 2 days. Relative expression to beta-actin. Error bars are SD from technical duplicates.
(K) Immunoblot analysis of phospho-Smad2. Cells were passaged once with low (3 ng/ml) or high (20 ng/ml) activin A before assay.