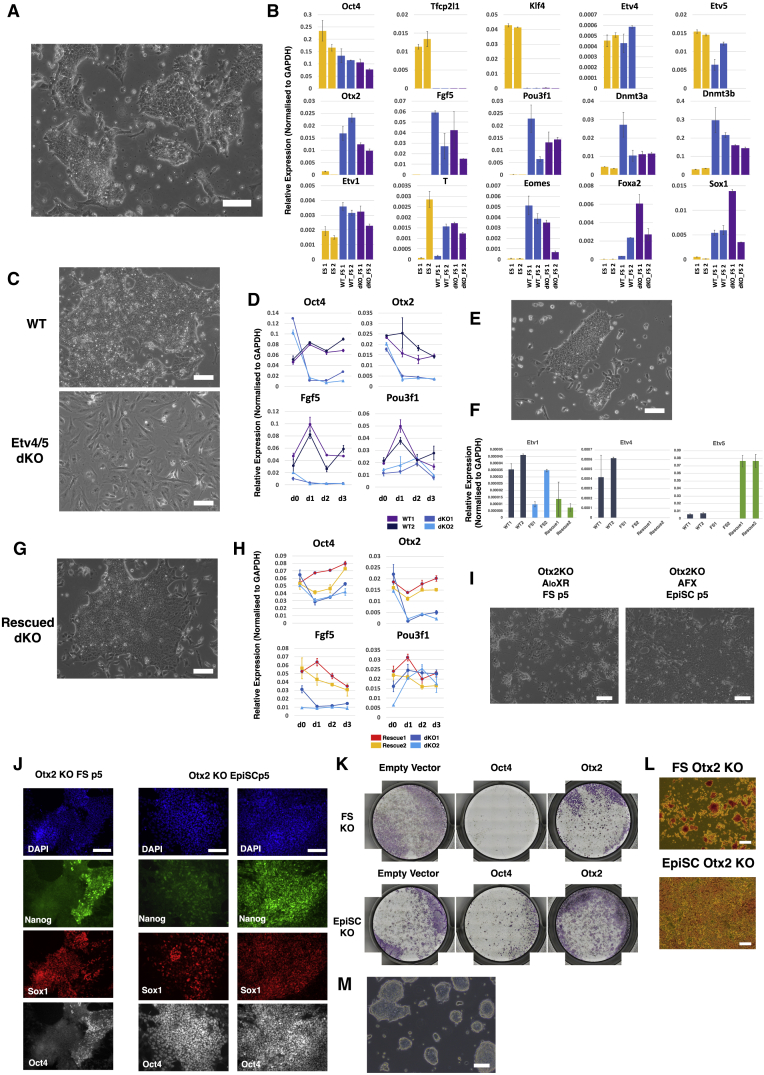
Figure 6.
Differential Requirements for Etv4/5 and Otx2
(A) Morphology of Etv4/5 dKO FS cells.
(B) qRT-PCR analysis of ESCs (yellow), parental (wild-type [WT]) FS cells (blue), and Etv4/5dKO FS cells (purple). Error bars represent SD from technical duplicates.
(C) Morphology of WT and dKO FS cells in EpiSC (AFX) culture medium for 3 days.
(D) Time course qRT-PCR analysis of WT and Etv4/5dKO FS cells in EpiSC (AFX) culture. Error bars are SD from technical duplicates.
(E) Morphology of Etv4/5dKO FS cells expressing Etv5 transgene.
(F) qRT-PCR assay of Etv1, -4, and -5 in Etv5 rescue dKO lines. Error bars represent SD from technical duplicates.
(G) Morphology of rescued dKO FS cells in EpiSC (AFX) culture.
(H) Time course qRT-PCR analysis of rescued lines. Error bars represent SD from technical duplicates.
(I) Phase images of Otx2 KO ESCs transferred to FS cell or EpiSC (AFX) culture conditions for 5 passages.
(J) Immunostaining of Otx2 KO cells at passage 5 (p5) in FS cell or EpiSC culture. Two classes of EpiSC colony were observed: left, homogeneous Oct4 with heterogenous Nanog and Sox1; right, uniformly Oct4, Sox1, and Nanog triple positive.
(K) Alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining of control and Oct4 and Otx2 KOs generated by Cas9/guide RNA (gRNA) transfection in FS cells and EpiSCs. Colonies were stained 3 days after replating transfected cells.
(L) Morphology of AP-positive Otx2 KO FS cells and EpiSCs.
(M) Representative image of Otx2 KO FS cells before culture collapse. Scale bars, 100 μm, except (J) 50 μm.