Figure 6.
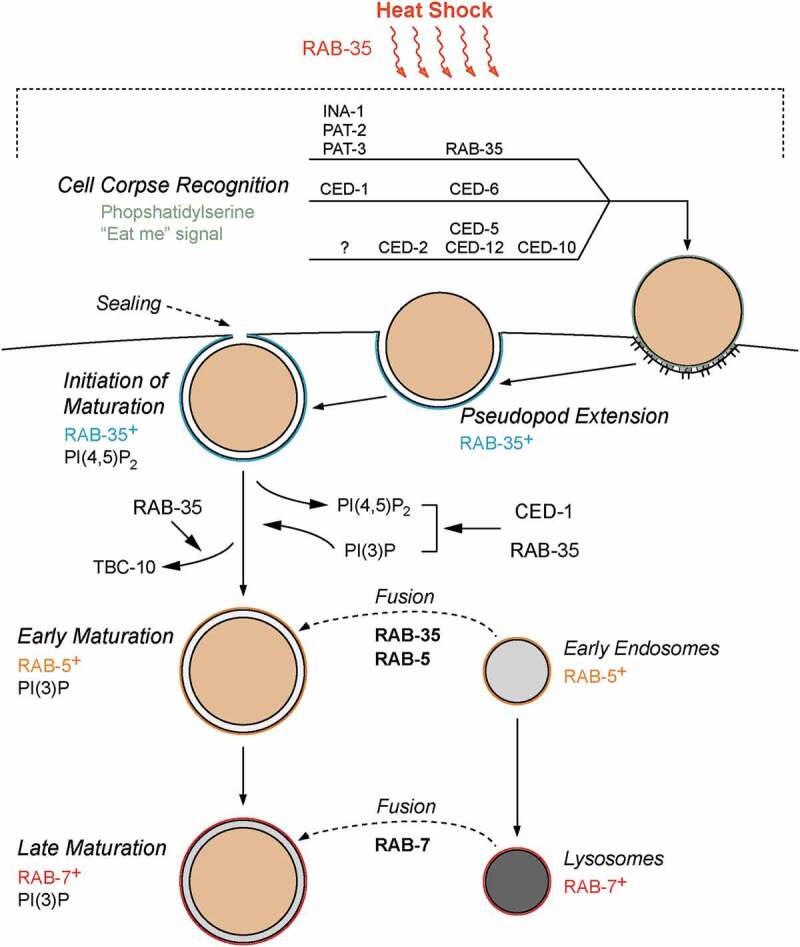
Model of RAB-35 action during apoptotic cell clearance
Diagram illustrating the various roles of RAB-35 during the recognition of apoptotic cells and the subsequent phagosome maturation and cell corpse degradation. See the ‘Discussion’ section for more details. During physiologically stressful conditions such as heat stress, RAB-35 functions to maintain the proper apoptotic cell clearance activity. RAB-35, CED-1, and CED-5 function redundantly in cell corpse recognition, while RAB-35 and CED-1 function redundantly throughout phagosome maturation. rab-35 functions in the same pathway as the integrins ina-1, pat-2, and pat-3, and in parallel to the canonical pathways ced-1/ced-6/ced-7/dyn-1 and ced-2/ced-5/ced-10/ced-12 [27]. CED-1, INA-1, PAT-2, and PAT-3 are all transmembrane receptors that recognize phosphatidylserine, an ‘eat-me’ signal exhibited by apoptotic cells that initiates engulfment. A question mark depicts that the identity of the candidate receptor activating the ced-5 pathway is still unclear. RAB-35 can be observed on the growing pseudopods alongside PI(4,5)P2, and plays a critical role in the initiation of phagosomal maturation and the removal of its GAP TBC-10. Furthermore, RAB-35 and CED-1 redundantly promote the removal of PI(4,5)P2 from, the production of PI(3)P on, and the recruitment of RAB-5 to the phagosomal membrane. RAB-35 and CED-1 were also found to independently promote the fusion of early endosomes to phagosomes, a process that is mediated by RAB-5 and PI(3)P.
