Figure 2.
Current COVID-19 Vaccine Candidates and Strategies for Developing Pan-β-CoV-B Vaccines
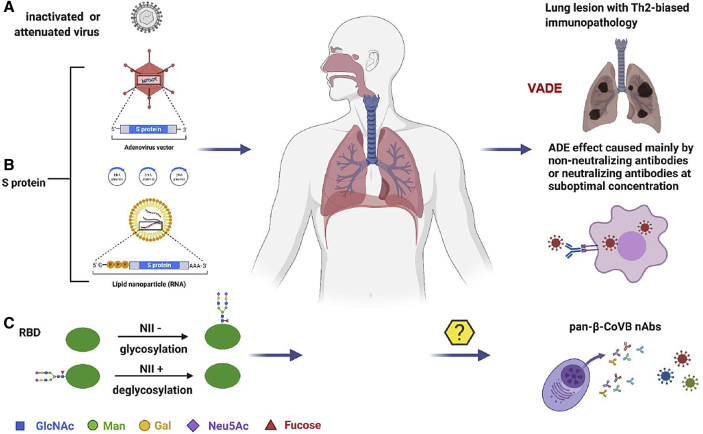
The antigens in the current COVID-19 vaccine candidates under clinical development consist of (A) whole viral particles either inactivated or attenuated, (B) spike (S) protein, or (C) receptor-binding domain (RBD). The vaccine-associated disease enhancement (VADE), including Th2-biased immunopathology and antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE), may occur when vaccinated people become naturally infected (Su et al., 2020). Pan-βCoVB vaccines can be designed using the strategies of glycosylation of NII-negative (NII−) sites and/or deglycosylation of the NII-positive (NII+) sites on S protein RBD. These optimized RBDs can also be used for the development of pan-β-CoV-B nAbs. Illustration created by the authors using http://www.biorender.com.