Figure 2.
Loss of Rbbp4 results in aberrant expression of ESC core pluripotency factors and differentiation-associated genes
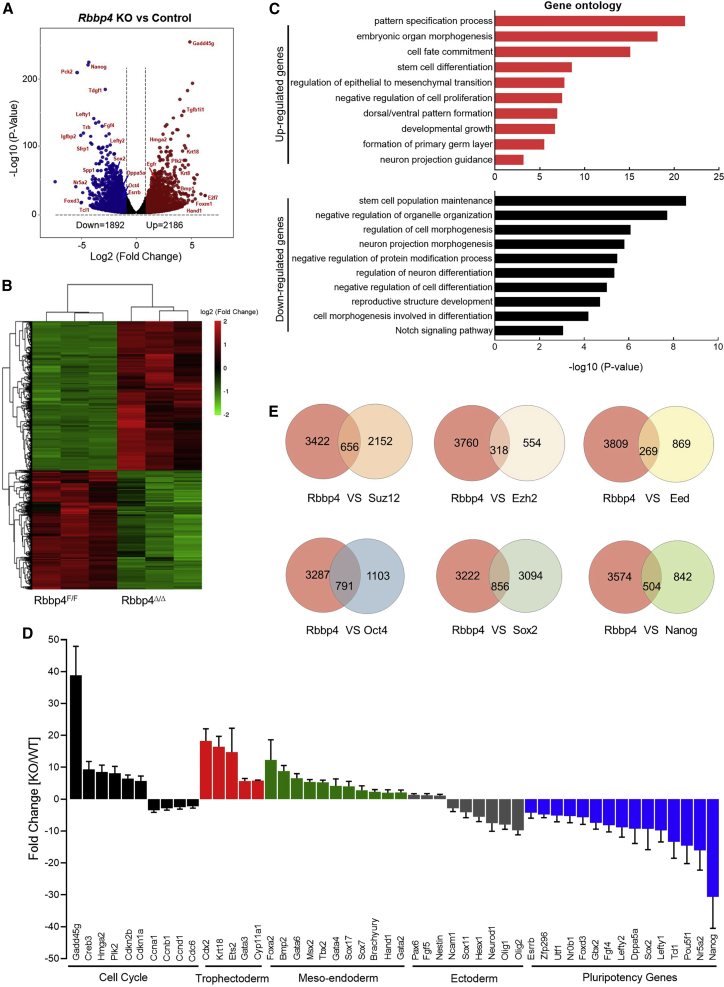
(A) Volcano plot showing the distribution of the differentially expressed (DE) genes with 2-fold changes upon Rbbp4 deletion. p < 0.05. Up- and downregulated genes are colored red and blue, respectively.
(B) Heatmap illustrating the RNA expression in Rbbp4F/F and Rbbp4Δ/Δ ESCs of RNA-seq analysis for 2-fold expression differentially expressed genes. False discovery rate < 0.05. Up- and downregulated genes are reported as red and green, respectively.
(C) Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analyses for biological processes associated with genes differentially expressed upon Rbbp4 deletion in ESCs. Analysis was carried out using Metascape (Zhou et al., 2019).
(D) Validation of RNA-seq data by qRT-PCR analysis. Relative mRNA levels of indicated cell-cycle-related genes, lineage-specific genes, and pluripotency-related genes in Rbbp4F/F after 3 days of Cre transfection were measured and data were normalized to β-actin relative to Rbbp4F/F. Data are pooled from three independent experiments and the error bars represent standard deviation of triplicate qPCR data.
(E) Venn diagrams (top) showing the overlap of the target genes between Rbbp4 and the core subunits of the PRC2 complex, respectively (Das et al., 2015; Pasini et al., 2007). Venn diagrams (bottom) showing the numbers of the regulated genes between Rbbp4 and pluripotency markers (Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog) (Ding et al., 2015; Loh et al., 2006).
See also Figure S3.