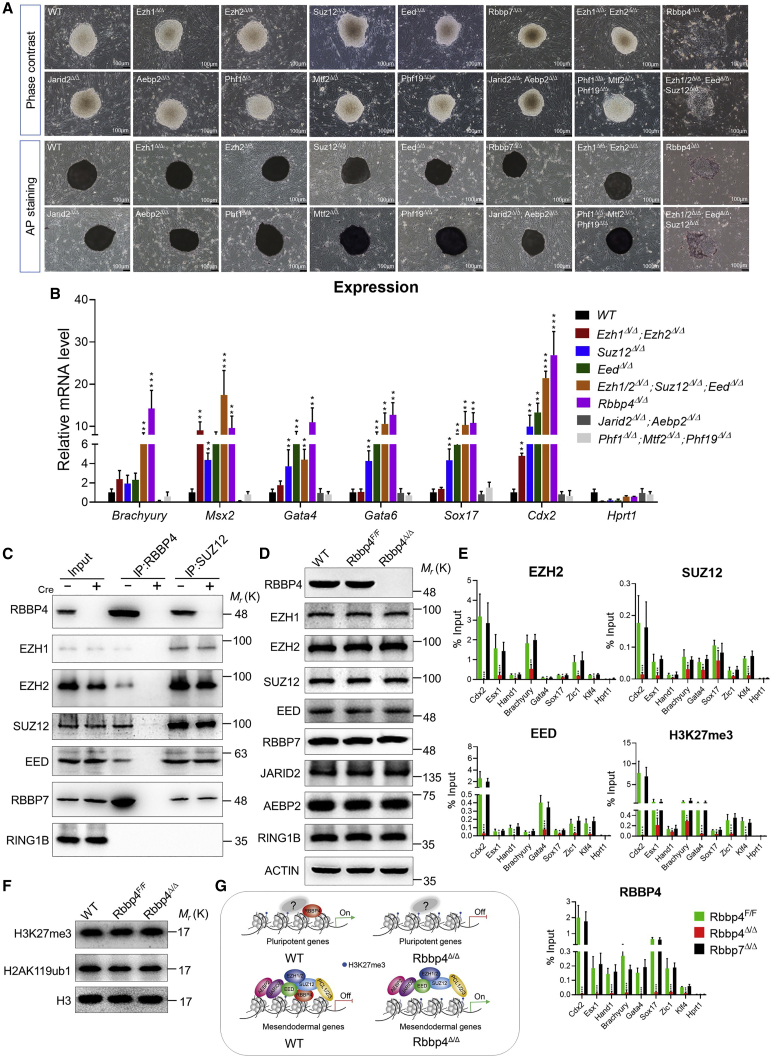
Figure 7.
RBBP4 guides PRC2 recruitment and H3K27 trimethylation at genomic loci
(A) Bright-field images of an ESC colony of wild-type and indicated genotypes after 7 days of culture. AP staining images of the ESC colony that arose from the wild-type and indicated genotypes. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(B) qRT-PCR quantification of Rbbp4 targets in indicated cell lines normalized to β-actin. Hprt1 is represented as a negative control.
(C) Endogenous coimmunoprecipitations of RBBP4 and SUZ12 in Rbbp4F/F transfected with Cre (+) or control vector (−) for 72 h, followed by western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies against core subunits of PRC2.
(D) Western blot analyses using the indicated antibodies against PRC2 subunits on whole-cell lysates from wild-type (WT), Rbbp4F/F, and Rbbp4Δ/Δ ESCs.
(E) ChIP-qPCR analysis of EZH2, SUZ12, EED, H3K27me3, and RBBP4 binding at the indicated regions of pluripotent transcription factors and mesendodermal genes (normalized to input) in Rbbp4F/F, Rbbp7Δ/Δ, or Rbbp4F/F ESCs that were transfected with Cre after 3 days.
(F) Western blot for H3K27 tri-methylation and H2AK119 mono-ubiquitination on nuclear lysates from Rbbp4Δ/Δ and matched control ESCs. Histone 3 was used as a loading control.
(G) Proposed model of Rbbp4-mediated pluripotency maintenance of ESCs.
Data in (B and E) represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Student's t test) compared with the control. See also Figures S5 and S6.