Figure 2.
Analyses of Molecular Features of L-ESCs
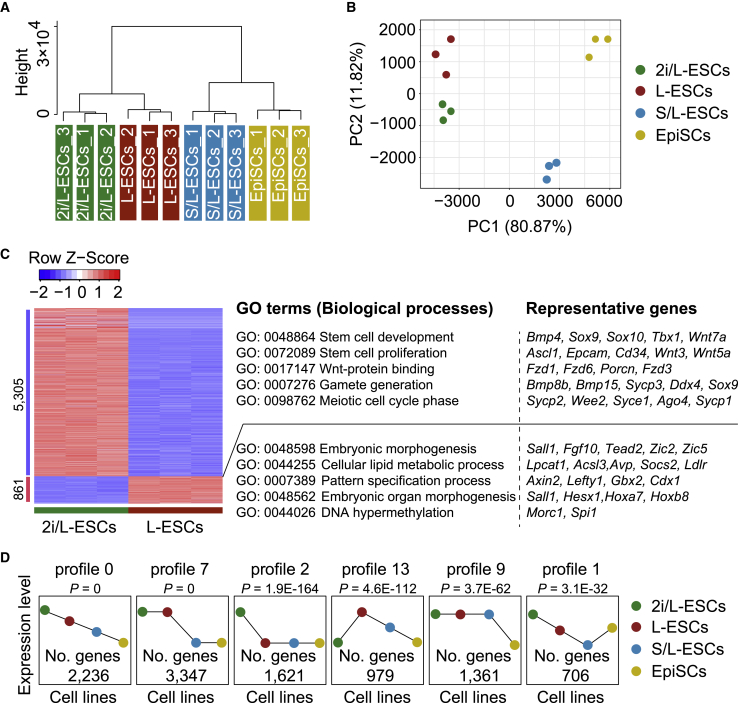
(A) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of the transcriptome from three biological replicates (n = 3) of four pluripotent stem cell lines.
(B) Principal component analysis of gene expression from the transcriptomes of three biological replicates (n = 3) of four pluripotent stem cells.
(C) Heatmap showing differentially expressed genes (mean log2(normalized read counts) > 2, log2(fold change) > 2, adjusted p < 0.05) in L-ESCs (n = 3) compared with 2i/L-ESCs (n = 3). Significantly enriched gene ontology (GO) terms and representative genes in each cluster are listed on the right.
(D) Comparison of L-ESCs, 2i/L-ESCs, S/L-ESCs, and EpiSCs. Among differentially expressed genes, a total of 3,347 genes (profile 7) were significantly highly expressed in L-ESCs and 2i/L-ESCs compared with S/L-ESCs and EpiSCs; a total of 1,621 genes (profile 2) were significantly upregulated in 2i/L-ESCs compared with L-ESCs, S/L-ESCs, and EpiSCs (n = 3 biological replicates of four pluripotent stem cell lines).