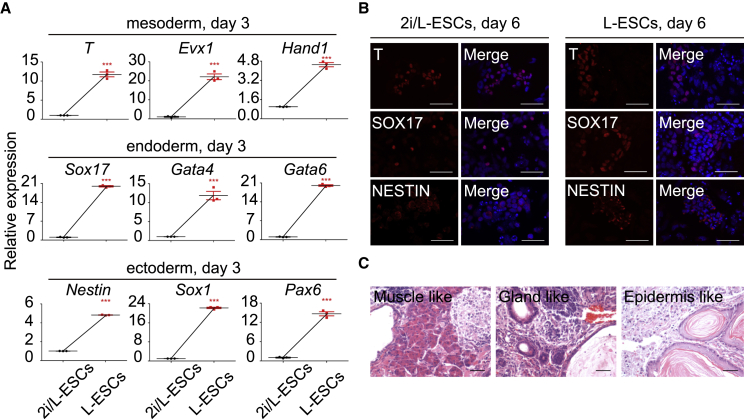
Figure 6.
In Vitro and In Vivo Differentiation Ability of L-ESCs
(A) Relative expression of mesoderm, endoderm, and ectoderm genes measured by qPCR, after L-ESCs underwent 3 days of in vitro differentiation. Error bars are mean ± SD (n = 3). The p values were calculated by two-tailed Student's t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.05.
(B) Immunostaining of T, SOX17, and NESTIN, after 2i/L-ESCs and L-ESCs underwent 6 days of in vitro differentiation (results of three independent experiments). Scale bars, 50 μm.
(C) Mature teratomas from L-ESCs. Left: mesoderm, muscle-like cells. Middle: endoderm, gland-like cells. Right: ectoderm, epidermis-like cells. The sections were stained with H&E (results of three independent experiments). Scale bars, 50 μm.